https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-04954-1
Regular Article
Elastic collision rates of spin-polarized fermions in two dimensions
1
Department of Physics and Applied Mathematics, Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Science (PIEAS), 45650, Nilore, Islamabad, Pakistan
2
Department of Physics, University of Mianwali, 42200, Mianwali, Pakistan
3
Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 2-12-1 O-okayama, 152-8550, Meguro, Tokyo, Japan
4
Center for Mathematical Sciences, PIEAS, 45650, Nilore, Islamabad, Pakistan
Received:
28
September
2023
Accepted:
29
January
2024
Published online:
15
February
2024
We study the p-wave elastic collision rates in a two-dimensional spin-polarized ultracold Fermi gas in the presence of a p-wave Feshbach resonance. We derive the analytical relation of the elastic collision rate coefficient in the close vicinity of resonance when the effective range is dominant. The elastic collision rate is enhanced by an exponential scaling of 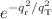 towards the resonance. Here,
towards the resonance. Here, 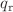 is the resonant momentum and
is the resonant momentum and 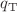 is the thermal momentum. An analogous expression derived for the case of three dimensions successfully explains the thermalization rates measurement in the recent experiment (Phys Rev A 88:012710, 2013). In the zero-range limit where the effective range is negligible, the elastic collision rate coefficient is proportional to temperature
is the thermal momentum. An analogous expression derived for the case of three dimensions successfully explains the thermalization rates measurement in the recent experiment (Phys Rev A 88:012710, 2013). In the zero-range limit where the effective range is negligible, the elastic collision rate coefficient is proportional to temperature 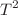 and scattering area
and scattering area 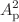 . Using these elastic collision rates, we studied the energy transfer from high to low velocity through p-wave collision. We also discuss the collisional stability in the presence of three-body losses in the background scattering limit. Our results may provide insight into the dynamics of the two-dimensional spin-polarized ultracold Fermi gas.
. Using these elastic collision rates, we studied the energy transfer from high to low velocity through p-wave collision. We also discuss the collisional stability in the presence of three-body losses in the background scattering limit. Our results may provide insight into the dynamics of the two-dimensional spin-polarized ultracold Fermi gas.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




