https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03006-w
Regular Article
Effect of non-thermal and non-extensive parameters on electron plasma waves in hybrid Cairns–Tsallis distributed plasmas
1
Department of Physics and Applied Mathematics (DPAM), PIEAS, P .O. Nilore, 44000, Islamabad, Pakistan
2
Center of Mathematical Sciences (CMS), PIEAS, P .O. Nilore, 44000, Islamabad, Pakistan
3
Department of Nuclear Engineering (DNE), PIEAS, P .O. Nilore, 44000, Islamabad, Pakistan
4
Theoretical Physics Division (TPD), PINSTECH, P .O. Nilore, 44000, Islamabad, Pakistan
Received:
3
February
2022
Accepted:
23
June
2022
Published online:
8
July
2022
Propagation and damping of high-frequency electron plasma or Langmuir waves (LWs) in hybrid non-thermal Cairns–Tsallis distributed plasmas (CTDP) are studied (numerically and analytically) under the well-known plasma kinetic approach based on a system of Vlasov–Poisson’s equations. For such system, that is a hybrid CTDP, the longitudinal dielectric response function is derived from a 1D-reduced Cairns–Tsallis distribution function, for both super-extensive (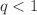 ) and sub-extensive (
) and sub-extensive (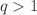 ) cases. It reveals the effects of the simultaneous presence of non-thermal (
) cases. It reveals the effects of the simultaneous presence of non-thermal (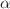 ) and non-extensive (q) parameters on damping rate and real frequency of LWs in hybrid CTDP. It is observed that on increasing value of non-thermal parameter (
) and non-extensive (q) parameters on damping rate and real frequency of LWs in hybrid CTDP. It is observed that on increasing value of non-thermal parameter (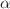 ) and decreasing the value of non-extensive parameter (q), the real frequency of LWs is increased in both the super- and sub-extensive plasmas. On the other hand, on decreasing the value of non-extensive parameter (q) damping rate of LWs is increased in both super-extensive and sub-extensive plasmas while on increasing the value of non-thermal parameter (
) and decreasing the value of non-extensive parameter (q), the real frequency of LWs is increased in both the super- and sub-extensive plasmas. On the other hand, on decreasing the value of non-extensive parameter (q) damping rate of LWs is increased in both super-extensive and sub-extensive plasmas while on increasing the value of non-thermal parameter (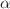 ) strong wave damping is observed in super-extensive case and the weak damping effect is found in sub-extensive plasma case. The present results (for hybrid CTDP) are distinguished from other non-thermal plasma distributions such as only Cairns or q-nonextensive plasmas. This study is utilitarian for different space plasma regions where the non-thermal and non-extensive plasma species exist.
) strong wave damping is observed in super-extensive case and the weak damping effect is found in sub-extensive plasma case. The present results (for hybrid CTDP) are distinguished from other non-thermal plasma distributions such as only Cairns or q-nonextensive plasmas. This study is utilitarian for different space plasma regions where the non-thermal and non-extensive plasma species exist.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022




