https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05853-1
Regular Article
Comparing effective temperatures in standard, Tsallis, and q-dual statistics from transverse momentum spectra of identified light charged hadrons produced in gold–gold collisions at RHIC energies
1
State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and Quantum Optics Devices & Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Institute of Theoretical Physics, Shanxi University, 030006, Taiyuan, China
2
Department of Physics, Xinzhou Normal University, 034000, Xinzhou, China
3
Department of Science Teaching, Beijing Vocational College of Agriculture, 102442, Beijing, China
4
Laboratory of High Energy Physics, Physical-Technical Institute of Uzbekistan Academy of Sciences, Chingiz Aytmatov Str. 2b, 100084, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
5
Department of Natural Sciences, National University of Science and Technology MISIS (NUST MISIS), Almalyk Branch, 110105, Almalyk, Uzbekistan
a fuhuliu@163.com, fuhuliu@sxu.edu.cn
b khkolimov@gmail.com, kh.olimov@uzsci.net
Received:
8
July
2024
Accepted:
16
November
2024
Published online:
5
December
2024
This study investigates the transverse momentum (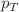 ) spectra of identified light charged hadrons produced in gold–gold (Au+Au) collisions across various centrality classes at center-of-mass energies per nucleon pair,
) spectra of identified light charged hadrons produced in gold–gold (Au+Au) collisions across various centrality classes at center-of-mass energies per nucleon pair, 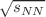 , ranging from 7.7 to 200 GeV, as measured by the STAR Collaboration at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC). The analysis employs standard (Bose-Einstein/Fermi-Dirac), Tsallis, and q-dual statistics to fit the same
, ranging from 7.7 to 200 GeV, as measured by the STAR Collaboration at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC). The analysis employs standard (Bose-Einstein/Fermi-Dirac), Tsallis, and q-dual statistics to fit the same 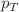 spectra and derive distinct effective temperatures:
spectra and derive distinct effective temperatures:  ,
,  , and
, and  . In most instances, there exists an approximately linear relationship or positive correlation between
. In most instances, there exists an approximately linear relationship or positive correlation between  and
and  , as well as between
, as well as between  and
and  , when considering
, when considering  as a baseline. However, while both
as a baseline. However, while both  and
and  increase from semi-central to central Au+Au collisions at 62.4 GeV and 200 GeV, where QGP is expected, changes in
increase from semi-central to central Au+Au collisions at 62.4 GeV and 200 GeV, where QGP is expected, changes in  occur more gradually. This work suggests that
occur more gradually. This work suggests that  is better suited for characterizing phase transitions between hadronic matter and QGP compared to
is better suited for characterizing phase transitions between hadronic matter and QGP compared to  or
or  , primarily due to the considerations related to entropy index in the Tsallis and q-dual statistics.
, primarily due to the considerations related to entropy index in the Tsallis and q-dual statistics.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.





