https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04002-4
Regular Article
Analysis of properties of the charged-particle jets in pp collisions at 13 TeV using non-extensive Tsallis statistics
1
Department of Physics, COMSATS University Islamabad campus, 44000, Islamabad, Pakistan
2
Physical-Technical Institute of Uzbekistan Academy of Sciences, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
3
National University of Science and Technology MISIS (NUST MISIS), Almalyk branch, Almalyk, Uzbekistan
a
uzma.tabassam@comsats.edu.pk
Received:
20
October
2022
Accepted:
17
April
2023
Published online:
8
May
2023
The ALICE collaboration at LHC has recently measured the inclusive charged-particle jets production with different resolution parameters of 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6 and 0.7 in pp collisions at 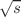 = 13 TeV in the transverse momentum range of
= 13 TeV in the transverse momentum range of  GeV/c and pseudorapidity range of
GeV/c and pseudorapidity range of  . In this work, we have fitted the inclusive charged-particles jet production measured by the ALICE Collaboration by the Tsallis function with thermodynamical consistence to measure the freeze-out parameters: effective temperature (
. In this work, we have fitted the inclusive charged-particles jet production measured by the ALICE Collaboration by the Tsallis function with thermodynamical consistence to measure the freeze-out parameters: effective temperature ( ), chemical potential (
), chemical potential ( ) and non-extensive parameter (q). The quality of the Tsallis fits with fixed
) and non-extensive parameter (q). The quality of the Tsallis fits with fixed  = 0 chemical potential has proved to be significantly better than those with fitted
= 0 chemical potential has proved to be significantly better than those with fitted  value. The fit parameters, q and
value. The fit parameters, q and  measure the degree of deviation from the equilibrium state and the effective temperature of the thermalized system, respectively. We have established the dependence of the effective temperature,
measure the degree of deviation from the equilibrium state and the effective temperature of the thermalized system, respectively. We have established the dependence of the effective temperature,  , and non-extensive parameter, q, on the value of the jet resolution parameter, R. We found out that the effective temperature,
, and non-extensive parameter, q, on the value of the jet resolution parameter, R. We found out that the effective temperature,  , of the Tsallis function shows a steady rise with increasing the jet resolution parameter. Also, a decrease in the non-extensive parameter q has been observed when the jet resolution parameter increases.
, of the Tsallis function shows a steady rise with increasing the jet resolution parameter. Also, a decrease in the non-extensive parameter q has been observed when the jet resolution parameter increases.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




