https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05860-2
Regular Article (incl. Technical & Progress Reports)
Optimal photovoltaic location selection systems through TOPSIS, AHP, and GIS techniques: a case study in Pakistan
Department of Mathematics, Abdul Wali Khan University, Garden Campus, 23200, Mardan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
Received:
29
February
2024
Accepted:
19
November
2024
Published online:
6
December
2024
There are various methods for energy production, such as hydro power, nuclear plants, and coal plants, but some of these sources emit 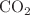 , posing harm to the environment. Consequently, the global trend is shifting towards renewable energy sources that have minimal environmental impact. The photovoltaic (PV) system is a notable renewable energy source as it generates power without harmful emissions. However, the effectiveness of a PV system varies based on location. This study presents a decision-making procedure to identify an optimal location for a photovoltaic (PV) system in Pakistan. Initially, a geographic information system (GIS)-based multi-criteria decision-making technique is employed to identify factors influencing the selection of an optimal PV system location. An analytic hierarchy process is then utilized to create a comparison decision matrix, balancing four primary criteria and ten sub-criteria, providing a comprehensive evaluation of potential sites. Ten cities across Pakistan, each with a population exceeding 300,000, are selected for assessment. These cities are evaluated and categorized using the Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) approach. The results indicate that Karachi is the ideal site for a PV system. This analytical approach aids in early planning, facilitating the identification of optimal locations for PV systems in Pakistan.
, posing harm to the environment. Consequently, the global trend is shifting towards renewable energy sources that have minimal environmental impact. The photovoltaic (PV) system is a notable renewable energy source as it generates power without harmful emissions. However, the effectiveness of a PV system varies based on location. This study presents a decision-making procedure to identify an optimal location for a photovoltaic (PV) system in Pakistan. Initially, a geographic information system (GIS)-based multi-criteria decision-making technique is employed to identify factors influencing the selection of an optimal PV system location. An analytic hierarchy process is then utilized to create a comparison decision matrix, balancing four primary criteria and ten sub-criteria, providing a comprehensive evaluation of potential sites. Ten cities across Pakistan, each with a population exceeding 300,000, are selected for assessment. These cities are evaluated and categorized using the Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) approach. The results indicate that Karachi is the ideal site for a PV system. This analytical approach aids in early planning, facilitating the identification of optimal locations for PV systems in Pakistan.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.





