https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05271-3
Regular Article
Combined analysis of midrapidity transverse momentum distributions of the charged pions and kaons, protons and antiprotons in p + Pb collisions at 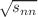 = 5.02 TeV at the LHC
= 5.02 TeV at the LHC
1
Physical-Technical Institute of Uzbekistan Academy of Sciences, Chingiz Aytmatov Str. 2B, 100084, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2
New Uzbekistan University, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
3
Institute of Physics and Technology, Satbayev University, Almaty, Kazakhstan
4
National University of Science and Technology MISIS (NUST MISIS), Almalyk Branch, Almalyk, Uzbekistan
5
Institute of Nuclear Physics, Almaty, Kazakhstan
6
Institute of Theoretical Physics, Shanxi University, 030006, Taiyuan, China
7
Samarkand State University Named After Sh. Rashidov, Samarkand, Uzbekistan
8
Institute of Nuclear Physics of Uzbekistan Academy of Sciences, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
a khkolimov@gmail.com, kh.olimov@uzsci.net
Received:
22
February
2024
Accepted:
10
May
2024
Published online:
30
May
2024
The experimental midrapidity transverse momentum spectra of the charged pions and kaons, protons and antiprotons in seven centrality classes of p + Pb collisions at 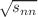 = 5.02 TeV, measured by the ALICE Collaboration, have been described quite well using simultaneous minimum χ2 fits by thermodynamically consistent as well as non-consistent Tsallis function with incorporated transverse flow. The border (threshold) value of the average number of participant nucleons, where the transverse radial flow starts emerging in p + Pb collisions at
= 5.02 TeV, measured by the ALICE Collaboration, have been described quite well using simultaneous minimum χ2 fits by thermodynamically consistent as well as non-consistent Tsallis function with incorporated transverse flow. The border (threshold) value of the average number of participant nucleons, where the transverse radial flow starts emerging in p + Pb collisions at 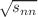 = 5.02 TeV, has been estimated to be
= 5.02 TeV, has been estimated to be 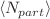 = 4.0 ± 0.5. The values of kinetic freeze-out temperature, T0, increase with an increase in
= 4.0 ± 0.5. The values of kinetic freeze-out temperature, T0, increase with an increase in 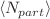 in region up to
in region up to 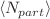 ≈ 4 and remain constant within uncertainties, showing a plateau, in region
≈ 4 and remain constant within uncertainties, showing a plateau, in region 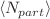 > 4 in p + Pb collisions at
> 4 in p + Pb collisions at 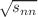 = 5.02 TeV. The behavior of the freeze-out temperature, T0, versus collision centrality (versus
= 5.02 TeV. The behavior of the freeze-out temperature, T0, versus collision centrality (versus 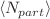 ), in p + Pb collisions at
), in p + Pb collisions at 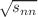 = 5.02 TeV proved to be similar to the dependence of T0 on charged-particle multiplicity density at midrapidity in p + p collisions at (s)1/2 = 7 and 13 TeV at the LHC. Non-extensivity parameter q has decreased consistently for all analyzed particle species with an increase in
= 5.02 TeV proved to be similar to the dependence of T0 on charged-particle multiplicity density at midrapidity in p + p collisions at (s)1/2 = 7 and 13 TeV at the LHC. Non-extensivity parameter q has decreased consistently for all analyzed particle species with an increase in 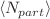 , suggesting that the degree of the system thermalization and equilibrium increases with increasing centrality of p + Pb collisions. Non-extensivity parameter q has been strongly anticorrelated with parameter
, suggesting that the degree of the system thermalization and equilibrium increases with increasing centrality of p + Pb collisions. Non-extensivity parameter q has been strongly anticorrelated with parameter 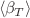 as well as
as well as 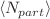 for all analyzed particle species. We have observed very strong positive correlation between parameter q for the charged pions and q for the charged kaons, which could be due to strong resemblance of the mechanisms of production of pions and kaons, which have similar structure consisting of one quark and one antiquark. The positive correlation between q (pions) and q ((anti)protons) as well as between q (kaons) and q ((anti)protons) has been also quite strong. The correlations among parameters q of the analyzed particle species in p + Pb collisions have been very similar to those observed earlier in high-energy Pb + Pb collisions and differed significantly from those in proton-proton collisions at the LHC.
for all analyzed particle species. We have observed very strong positive correlation between parameter q for the charged pions and q for the charged kaons, which could be due to strong resemblance of the mechanisms of production of pions and kaons, which have similar structure consisting of one quark and one antiquark. The positive correlation between q (pions) and q ((anti)protons) as well as between q (kaons) and q ((anti)protons) has been also quite strong. The correlations among parameters q of the analyzed particle species in p + Pb collisions have been very similar to those observed earlier in high-energy Pb + Pb collisions and differed significantly from those in proton-proton collisions at the LHC.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




