https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05012-6
Regular Article
Insight on the optoelectronic properties of novel quaternary Ge–Se–Tl–Sb non-crystalline glassy alloy films for optical fiber sensing devices
Department of Physics, Faculty of Education, Ain Shams University, 11566, Cairo, Egypt
Received:
5
October
2023
Accepted:
16
February
2024
Published online:
4
March
2024
Chalcogenide glass (Ge0.1Se0.7Tl0.2)85Sb15 is synthesized in bulk form by the melt quenching method and thermally evaporated as thin films. The amorphous character of the studied films is examined by XRD analysis. The values of refractive index ( ) and extinction index (
) and extinction index ( ) are estimated from transmittance
) are estimated from transmittance 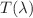 data using Swanepoel’s method and are found to be thickness independent. The values of the indirect optical band gap (
data using Swanepoel’s method and are found to be thickness independent. The values of the indirect optical band gap (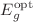 ) and Urbach tail (
) and Urbach tail (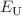 ) energies are 1.164 eV and 0.176 eV, respectively. The optical
) energies are 1.164 eV and 0.176 eV, respectively. The optical  and electrical
and electrical  conductivities of (Ge0.1Se0.7Tl0.2)85Sb15 films increase while the penetration depth
conductivities of (Ge0.1Se0.7Tl0.2)85Sb15 films increase while the penetration depth  decreases with photon energy (
decreases with photon energy ( ). The Wemple-DiDomenico (WDD) oscillator model calculates optical parameters such as single-oscillator
). The Wemple-DiDomenico (WDD) oscillator model calculates optical parameters such as single-oscillator  and strength
and strength  energies, lattice dielectric constant
energies, lattice dielectric constant  and ratio
and ratio 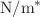 . The calculated values of third-order susceptibility
. The calculated values of third-order susceptibility  and nonlinear index of refraction
and nonlinear index of refraction  are 6.34 × 10–12 and 3.76 × 10–11
are 6.34 × 10–12 and 3.76 × 10–11  . Dielectric constant
. Dielectric constant 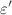 and loss
and loss  decrement with frequency and increment with temperature. The ac conductivity
decrement with frequency and increment with temperature. The ac conductivity  increases with frequency and temperature, which is proportional to
increases with frequency and temperature, which is proportional to  and the exponent
and the exponent  decreases with temperature. The obtained results of
decreases with temperature. The obtained results of  and
and  are interpreted via the correlated barrier hopping (CBH) model. Values of the density of localized states
are interpreted via the correlated barrier hopping (CBH) model. Values of the density of localized states 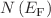 are enhanced with frequency and temperature. The results obtained suggest that
are enhanced with frequency and temperature. The results obtained suggest that 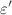 ,
,  ,
,  and
and 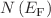 are improved by decreasing the film thickness. These research results emphasize the composition’s applicability for several optical potential applications, like optical fiber sensing devices, photo-detectors, and narrow band optical filters.
are improved by decreasing the film thickness. These research results emphasize the composition’s applicability for several optical potential applications, like optical fiber sensing devices, photo-detectors, and narrow band optical filters.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




