https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04753-0
Regular Article
Electronic properties of ionizing radiation-induced defects at SiO /Si interface associated with non-trivial excess current splitting
/Si interface associated with non-trivial excess current splitting
1
Institute of Electronic Engineering, China Academy of Engineering Physics, 621999, Mianyang, People’s Republic of China
2
Microsystem and Terahertz Research Center, China Academy of Engineering Physics, 610200, Chengdu, People’s Republic of China
3
School of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Shandong University, 266237, Qingdao, People’s Republic of China
4
College of Physics and Electronic Information Engineering, Neijiang Normal University, 641100, Neijiang, People’s Republic of China
g
kwungyusung@gmail.com
h
yangliuphy@gmail.com
Received:
7
August
2023
Accepted:
24
November
2023
Published online:
2
January
2024
Low dose rate radiation experiments on gate controlled lateral PNP (GLPNP) transistors show a non-trivial splitting of the peak of the base current at various gate bias. The absolute and relative values of the two peaks vary with respect to the dose and dose rate. Through analytical calculations and for the first time, the splitting of the peaks was found to be attributed to the different electron (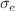 ) and hole (
) and hole (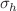 ) capture cross sections of the acceptor and donor-like defects formed on SiO
) capture cross sections of the acceptor and donor-like defects formed on SiO /Si interface. The results reveal that the ionizing radiation induces primarily two kinds of electronic active interface defects, which are different not only in the energy spectrum but also the
/Si interface. The results reveal that the ionizing radiation induces primarily two kinds of electronic active interface defects, which are different not only in the energy spectrum but also the 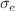 /
/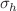 . Significantly,
. Significantly, 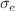 and
and 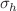 should not be simplified to one effective cross section as commonly treated, as their ratios play an essential role in determining the efficiency of e-h recombination with respect to the Fermi energy.
should not be simplified to one effective cross section as commonly treated, as their ratios play an essential role in determining the efficiency of e-h recombination with respect to the Fermi energy.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




