https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04596-9
Regular Article
Numerical and statistical analysis of transport performance of viscous flows over a wedge with heat transfer by using response surface methodology: sensitivity analysis
1
Centre for Mathematical Sciences, Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 45650, Nilore Islamabad, Pakistan
2
Department of Physics & Applied Mathematics, Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 45650, Nilore Islamabad, Pakistan
3
Department of Mathematics and Statistics, FBAS, International Islamic University Islamabad, H-10, 44000, Islamabad, Pakistan
4
Nonlinear Analysis and Applied Mathematics (NAAM)-Research Group, Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, King Abdulaziz University, P.O. Box 80203, 21589, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
Received:
20
September
2022
Accepted:
15
October
2023
Published online:
31
October
2023
In this study the sensitivity analysis of viscous flow past a symmetric wedge with thermal effect is studied numerically and statistically. The partial differential equations (PDEs) are transformed into nonlinear ordinary differential equation by using similarity transformations, and these transformed ODE's are solved with the help of MATLAB built-in code bvp4c. The numerical outcomes are compared with previous existing work and were found to be correct. Then, using response surface methodology (RSM) we developed a correlation between the independent parameters and dependent output responses. Using RSM we obtained the ANOVA results for the coefficient of determination for 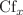 and
and  . The ANOVA shows the results of
. The ANOVA shows the results of 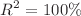 and
and 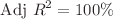 for
for 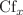 and
and 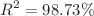 and
and 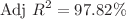 for
for 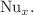 These results show the best correlation between input parameters and output responses. Then, we performed sensitivity analysis and found that the Falkner–Skan exponent (m) is more sensitive to the skin friction coefficient
These results show the best correlation between input parameters and output responses. Then, we performed sensitivity analysis and found that the Falkner–Skan exponent (m) is more sensitive to the skin friction coefficient 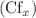 , while Prandtl number (Pr) is more sensitive to the Nusselt number
, while Prandtl number (Pr) is more sensitive to the Nusselt number 
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




