https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04335-0
Regular Article
Cosmographic implications of f(R, T) gravitation
1
Department of Physics, Istanbul University, Vezneciler, Fatih, 34134, Istanbul, Turkey
2
Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU), 13318, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
3
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University of Khartoum, P.O. Box 321, 11115, Khartoum, Sudan
4
Centre for Space Research, North-West University, 2520, Potchefstroom, South Africa
5
National Institute for Theoretical and Computational Sciences (NITheCS), 3201, Stellenbosch, South Africa
Received:
9
April
2023
Accepted:
31
July
2023
Published online:
9
August
2023
In this paper, we will explore the cosmological implications of the flat Friedmann–Robertson–Walker model within the context of 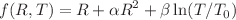 gravity, where R is the Ricci scalar, and T is the trace of the energy-momentum tensor. We prove that the generalized Friedmann equation has nonlinear differential equations of the third order when a nonlinear term is introduced into the f(R, T) formula. In redshift space, the modified theory’s field equations are converted into a coupled system of first-order differential equations. The current values of q, j, and s, the deceleration, the jerk, and the snap parameters from Planck 2018 are used as initial conditions with Runge–Kutta fourth-order method to solve for the model numerically. Our obtained model successfully explains the phase transition of the universe’s expansion (from an early decelerating phase to the late accelerating phase).
gravity, where R is the Ricci scalar, and T is the trace of the energy-momentum tensor. We prove that the generalized Friedmann equation has nonlinear differential equations of the third order when a nonlinear term is introduced into the f(R, T) formula. In redshift space, the modified theory’s field equations are converted into a coupled system of first-order differential equations. The current values of q, j, and s, the deceleration, the jerk, and the snap parameters from Planck 2018 are used as initial conditions with Runge–Kutta fourth-order method to solve for the model numerically. Our obtained model successfully explains the phase transition of the universe’s expansion (from an early decelerating phase to the late accelerating phase).
Alnadhief H. A. Alfedeel and Amare Abebe have equally contributed to this work.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




