https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04483-3
Regular Article
Constrained evolution of effective equation of state parameter in non-linear  dark energy model: insights from Bayesian analysis of cosmic chronometers and Pantheon samples
dark energy model: insights from Bayesian analysis of cosmic chronometers and Pantheon samples
1
L. N. Gumilyov Eurasian National University, 010008, Astana, Kazakhstan
2
Ratbay Myrzakulov Eurasian International Centre for Theoretical Physics, 010009, Astana, Kazakhstan
3
Quantum Physics and Magnetism Team, LPMC, Faculty of Science Ben M’sik, Casablanca Hassan II University, Casablanca, Morocco
4
Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU), 13318, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
5
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University of Khartoum, P.O. Box 321, 11115, Khartoum, Sudan
6
Centre for Space Research, North-West University, 2520, Potchefstroom, South Africa
7
National Institute for Theoretical and Computational Sciences (NITheCS), 3201, Stellenbosch, South Africa
Received:
3
July
2023
Accepted:
14
September
2023
Published online:
26
September
2023
We conduct a Bayesian analysis of recent observational datasets, specifically the Cosmic Chronometers (CC) dataset and Pantheon samples, to investigate the evolution of the EoS parameter in dark energy models. Our study focused on the effective EoS parameter, which is described by the parametric form 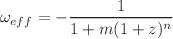 , where m and n are model parameters. This parametric form is applicable within the framework of
, where m and n are model parameters. This parametric form is applicable within the framework of 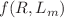 gravity, where R represents the Ricci scalar and
gravity, where R represents the Ricci scalar and 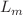 is the matter Lagrangian. Here, we examine a non-linear
is the matter Lagrangian. Here, we examine a non-linear 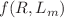 model characterized by the functional form
model characterized by the functional form 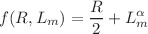 , where
, where 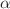 is the free parameter of the model. We examine the evolution of several cosmological parameters, including the effective EoS parameter
is the free parameter of the model. We examine the evolution of several cosmological parameters, including the effective EoS parameter 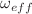 , the deceleration parameter q, the density parameter
, the deceleration parameter q, the density parameter 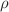 , the pressure p, and the statefinder parameters. Our analysis revealed that the constrained current value of the effective EoS parameter,
, the pressure p, and the statefinder parameters. Our analysis revealed that the constrained current value of the effective EoS parameter, 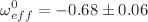 for both the CC and Pantheon datasets, points towards a quintessence phase. Moreover, at redshift
for both the CC and Pantheon datasets, points towards a quintessence phase. Moreover, at redshift 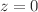 , the deceleration parameter,
, the deceleration parameter, 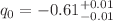 , indicates that the present Universe is undergoing accelerated expansion.
, indicates that the present Universe is undergoing accelerated expansion.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




