https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-03865-x
Regular Article
Mathematical model and analysis of monkeypox with control strategies
1
Department of Mathematical and Computer Sciences, University of Medical Sciences, Ondo City, Ondo State, Nigeria
2
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, University of Medical Sciences, Ondo City, Ondo State, Nigeria
3
Department of Mathematical Sciences, Federal University of Technology, Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria
4
Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of South Africa, Florida, South Africa
5
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Microbiology Division, Lenexa, KS, USA
6
Department of Mathematics, Osun State University Osogbo, Osogbo, Osun State, Nigeria
Received:
9
February
2023
Accepted:
5
March
2023
Published online:
14
March
2023
This paper takes into consideration the development and rigorous analysis of a compartmental mathematical model of monkeypox dynamics in the presence of quarantine and isolation compartments. The newly proposed model is governed by 7-dimensional system of ordinary differential equations which describes the monkeypox transmission and spread between the interacting populations of human and rodent. In view of positivity and boundedness of solutions, the model is shown to be mathematically well posed. The control monkeypox reproduction number, 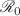 , is obtained using the next generation matrix approach. The threshold quantity is used to investigate the stability analysis of the monkeypox-free equilibrium. Further qualitative analysis suggests that the model undergoes the phenomenon of backward bifurcation in the presence of the fraction of exposed individuals that are quarantined (
, is obtained using the next generation matrix approach. The threshold quantity is used to investigate the stability analysis of the monkeypox-free equilibrium. Further qualitative analysis suggests that the model undergoes the phenomenon of backward bifurcation in the presence of the fraction of exposed individuals that are quarantined ( ) whenever
) whenever 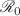 of the model is below unity. By employing center manifold theory, the possibility of ruling out the occurrence of backward bifurcation when
of the model is below unity. By employing center manifold theory, the possibility of ruling out the occurrence of backward bifurcation when 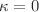 is shown. The global asymptotic behaviour of the model around the monkeypox-free equilibrium is established using Lyapunov function method. The respective sensitivity index of individual model parameter with respect to
is shown. The global asymptotic behaviour of the model around the monkeypox-free equilibrium is established using Lyapunov function method. The respective sensitivity index of individual model parameter with respect to 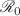 is obtained to gain epidemiological insights into intervention strategies for monkeypox prevention and control. The effects of variation in the effective contact rate of human to human and other key parameters on the disease transmission dynamics under different scenarios are demonstrated quantitatively. The findings of this study show that, we can attain a monkeypox-free state if quarantine and isolation guidelines are carefully followed, as well as preventative measures that minimize the effective contact rates between humans and rodents as well as between rodents and humans during the monkeypox outbreak.
is obtained to gain epidemiological insights into intervention strategies for monkeypox prevention and control. The effects of variation in the effective contact rate of human to human and other key parameters on the disease transmission dynamics under different scenarios are demonstrated quantitatively. The findings of this study show that, we can attain a monkeypox-free state if quarantine and isolation guidelines are carefully followed, as well as preventative measures that minimize the effective contact rates between humans and rodents as well as between rodents and humans during the monkeypox outbreak.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




