https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03505-w
Regular Article
Scattering of partially coherent anomalous hollow beams upon a random medium
Department of Applied Physics, East China Jiaotong University, 330013, Nanchang, China
Received:
29
September
2022
Accepted:
15
November
2022
Published online:
27
November
2022
In this paper, partially coherent anomalous hollow beams scattering from a quasi-homogeneous medium with semisoft boundary is investigated for the first time, based on the accuracy of the first-order Born approximation. Analytical expressions for the scattering spectral density is derived and influence of parameters of the incident optical beam and the scattering medium on the far-zone scattered field is studied in detail. Numerical simulation results indicate that the spectral density distribution of the scattered field is significantly affected by the transverse coherence width  of the incident beam, the eccentricity e of the incident beam, and the correlation length
of the incident beam, the eccentricity e of the incident beam, and the correlation length  of the scatterer. The scattering spectral degree of coherence is affected by the effective radius
of the scatterer. The scattering spectral degree of coherence is affected by the effective radius 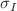 , the correlation length
, the correlation length  , and the edge softness N of the scatterer. It is noteworthy that the far-zone scattered field is coherent at the center of the scattered field. Moreover, the center of the scattered spectral intensity distribution does not have an elliptical solid after being scattered by a quasi-homogeneous medium, which is different from the propagation characteristics of anomalous hollow beams in other media. The spectral intensity distribution and spectral coherence obtained through numerical simulation in this paper could further enrich the scattering theory, and find applications in optical trapping of particles, medical diagnosis and obtaining the structure information of a quasi-homogeneous medium.
, and the edge softness N of the scatterer. It is noteworthy that the far-zone scattered field is coherent at the center of the scattered field. Moreover, the center of the scattered spectral intensity distribution does not have an elliptical solid after being scattered by a quasi-homogeneous medium, which is different from the propagation characteristics of anomalous hollow beams in other media. The spectral intensity distribution and spectral coherence obtained through numerical simulation in this paper could further enrich the scattering theory, and find applications in optical trapping of particles, medical diagnosis and obtaining the structure information of a quasi-homogeneous medium.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




