https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00615-1
Regular Article
Optimal control analysis of tuberculosis (TB) with vaccination and treatment
1
Department of Mathematics, University of Peshawar, Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
2
Department of Mathematics, City University of Science and Information Technology, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Peshawar, Pakistan
3
Informetrics Research Group, Ton Duc Thang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
4
Faculty of Mathematics and Statistics, Ton Duc Thang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
c
muhammad.altaf.khan@tdtu.edu.vn
Received:
19
May
2020
Accepted:
15
July
2020
Published online:
26
July
2020
Tuberculosis remains a major health challenge for the humans of the whole world, especially in developing countries including Pakistan. Despite being a preventable and curable disease, TB is still the world’s top infectious killer and among the leading diseases causing morbidity and mortality. In this paper, we formulate a deterministic model to study the dynamics and possible control of TB disease. Initially, we develop the model without control variables and present the basic mathematical analysis of the model. The stability results of the model at the disease-free case are presented when  and further it is proven that the infection will persist uniformly when
and further it is proven that the infection will persist uniformly when 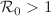 . The model biological parameters are estimated using the confirmed TB infected cases reported in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan, from 2002 to 2017. Based on the estimated and fitted parameters, we obtained that
. The model biological parameters are estimated using the confirmed TB infected cases reported in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan, from 2002 to 2017. Based on the estimated and fitted parameters, we obtained that 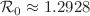 . The model stability is investigated graphically when
. The model stability is investigated graphically when 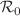 is greater or less than one. Further, the sensitivity analysis of the threshold parameter is performed in order to formulate an appropriate optimal strategy for curtailing the TB infection. Furthermore, we develop the control model using three control variables. The existence of the optimal control problem and the necessary mathematical results for the control characterizations is obtained. Finally, the simulations are presented to highlight the importance and impact of suggested control interventions on the disease dynamics. The proposed set of controls can be used for the elimination of TB infection in a community.
is greater or less than one. Further, the sensitivity analysis of the threshold parameter is performed in order to formulate an appropriate optimal strategy for curtailing the TB infection. Furthermore, we develop the control model using three control variables. The existence of the optimal control problem and the necessary mathematical results for the control characterizations is obtained. Finally, the simulations are presented to highlight the importance and impact of suggested control interventions on the disease dynamics. The proposed set of controls can be used for the elimination of TB infection in a community.
© Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020




