https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06625-1
Regular Article
Design of the geomagnetic field compensation system for hyper-Kamiokande
1
Departamento de Física, Universidad de Oviedo, Calvo Sotelo 18, 33007, Oviedo, Asturias, Spain
2
MOMA, Instituto Universitario de Ciencias y Tecnologías Espaciales de Asturias (ICTEA), Independencia 13, 33004, Oviedo, Asturias, Spain
3
Departamento de Explotación y prospección de Minas, Universidad de Oviedo, Independencia 13, 33004, Oviedo, Asturias, Spain
4
Departamento de Matemáticas, Universidad de Oviedo, Calvo Sotelo 18, 33007, Oviedo, Asturias, Spain
5
Departamento de Ingeniería Eléctrica, Electrónica, de Comunicaciones y de Sistemas, Universidad de Oviedo, Edificio Departamental Oeste, Módulo 2 - 1a Planta. Campus de Viesques, 33204, Gijón, Asturias, Spain
6
Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, The University of Tokyo, 5-1-5 Kashiwanoha, 277-8582, Kashiwa, Chiba, Japan
Received:
2
June
2025
Accepted:
4
July
2025
Published online:
23
July
2025
The Hyper-Kamiokande neutrino detector, is a next-generation facility designed to explore fundamental questions in particle physics. It faces challenges posed by the Earth’s magnetic field, which affects photomultiplier tube (PMT) efficiency. This study details the design and optimization of a geomagnetic field compensation system to mitigate these effects. A system of circular and rectangular compensation coils was developed and evaluated through simulations and experiments, prioritizing the minimization of residual perpendicular magnetic fields and maintaining high detection efficiency. The optimized configuration achieves an average residual field of 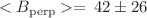 mG, with only 4.05% of PMTs experiencing fields above 100 mG, and results in minimal detection efficiency loss of
mG, with only 4.05% of PMTs experiencing fields above 100 mG, and results in minimal detection efficiency loss of 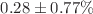 . Practical considerations, such as coil placement and current optimization, were addressed to ensure feasibility. This robust design enhances detector performance and supports hyper-Kamiokande’s mission to advance neutrino physics and investigate physics beyond the standard model.
. Practical considerations, such as coil placement and current optimization, were addressed to ensure feasibility. This robust design enhances detector performance and supports hyper-Kamiokande’s mission to advance neutrino physics and investigate physics beyond the standard model.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




