https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06616-2
Regular Article
Critical exponents, magnetic and thermodynamic properties of the mixed-spin Ising model with competing bulk and surface ordering: Monte Carlo simulation
1
LS2ME Laboratory, Polydisciplinary Faculty, Sultan Moulay Slimane University, 25000, Khouribga, Morocco
2
LPMC Laboratory, Theoretical Physics Group, Faculty of Sciences, Chouaïb Doukkali University, 24000, El Jadida, Morocco
3
Sorbonne Université, Université Paris Cité, Univ Paris Est Créteil, CNRS, IRD, INRAE, Institute of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, IEES Paris, 75005, Paris, France
Received:
7
April
2025
Accepted:
2
July
2025
Published online:
22
July
2025
In this study, we employed Monte Carlo simulations to investigate a three-dimensional mixed-spin Ising system, incorporating spins of 1/2 and 1 with competing exchange interactions between the surface and the bulk. We analyzed the impact of system size on the system’s magnetic and thermodynamic properties. Additionally, by examining the effect of the ratio 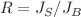 , which reflects the competition between surface exchange interaction (
, which reflects the competition between surface exchange interaction (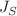 ) and bulk exchange interaction (
) and bulk exchange interaction (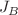 ), the study presented phase diagrams showing qualitatively interesting features, indicating that the system can undergo various phases and phase transitions. The results also revealed the existence of a compensation a precise within a specific range of R values. The values of the critical exponents associated with the spontaneous magnetization
), the study presented phase diagrams showing qualitatively interesting features, indicating that the system can undergo various phases and phase transitions. The results also revealed the existence of a compensation a precise within a specific range of R values. The values of the critical exponents associated with the spontaneous magnetization 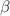 , the magnetic susceptibility
, the magnetic susceptibility 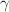 , and the specific heat
, and the specific heat 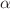 were accurately estimated for the surface case:
were accurately estimated for the surface case: 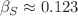 ,
, 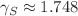 ,
, 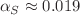 , and the bulk case:
, and the bulk case: 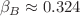 ,
, 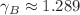 , and
, and 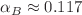 . These values were found to be in excellent agreement with the universal values of the two- and three-dimensional Ising model.
. These values were found to be in excellent agreement with the universal values of the two- and three-dimensional Ising model.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




