https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06464-0
Regular Article
Jeans mechanism in the context of modified Newton dynamics
Laboratoire LRPPS, Faculté des Mathématiques et des Sciences de la Matière, Université Kasdi Merbah Ouargla, 30000, Ouargla, Algeria
a hakim9502.benkrane@gmail.com, abdelhakim.benkrane@univ-ouargla.dz
Received:
13
January
2025
Accepted:
22
May
2025
Published online:
6
June
2025
This paper examines the Jeans mechanism within the framework of fractional gravity for 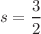 , which mimics MOND. We began by calculating the gravitational binding energy and expressing it as a function of
, which mimics MOND. We began by calculating the gravitational binding energy and expressing it as a function of  . We found that the gravitational binding energy vanishes at a specific value of
. We found that the gravitational binding energy vanishes at a specific value of  and increases for sufficiently large values of the cloud’s radius. Subsequently, we derived general expressions for the Jeans radius and Jeans mass and applied them to some known stellar systems, comparing the results with those obtained under Newtonian gravity. For instance, in the case of Bok globules, we found that the Jeans radius and Jeans mass are larger under MOND than under Newtonian gravity.
and increases for sufficiently large values of the cloud’s radius. Subsequently, we derived general expressions for the Jeans radius and Jeans mass and applied them to some known stellar systems, comparing the results with those obtained under Newtonian gravity. For instance, in the case of Bok globules, we found that the Jeans radius and Jeans mass are larger under MOND than under Newtonian gravity.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




