https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06299-9
Regular Article
 cosmology with the parametrization of H(z) parameter
cosmology with the parametrization of H(z) parameter
1
Department of Applied Sciences, The NorthCap University, 122017, Gurugram, India
2
Department of Physics, United College of Engineering and Research, 201310, Greater Noida, India
3
Department of Mathematics, S.P.M. Science and Gilani Arts and Commerce College, 445301, Ghatanji, Yavatmal, Maharashtra, India
4
L N Gumilyov Eurasian National University, 010008, Astana, Kazakhstan
Received:
22
January
2025
Accepted:
4
April
2025
Published online:
5
May
2025
Building FRW cosmological models within the context of the 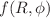 theory of gravity is our goal in this effort. We investigate the universe’s accelerating behavior for a specific form of the
theory of gravity is our goal in this effort. We investigate the universe’s accelerating behavior for a specific form of the 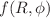 gravity model by employing a new, straightforward parametrization of the Hubble parameter in the form
gravity model by employing a new, straightforward parametrization of the Hubble parameter in the form ![$$H(z)=\frac{H_0}{\sqrt{2}}\left[ 1+(1+z)^{(2(1+\alpha )) } \right] ^{\frac{1}{2}}$$](/articles/epjplus/abs/2025/05/13360_2025_Article_6299/13360_2025_Article_6299_tex_eq5.png) . Using the
. Using the 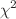 -minimization approach, we impose constraints on the related free parameters that are present in H(z) within the
-minimization approach, we impose constraints on the related free parameters that are present in H(z) within the 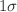 ,
, 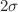 , and
, and 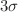 confidence bounds. It has been observed that the values obtained are all within the range that is indicated by cosmological observations. Through the utilization of the free parameter best-fit values, we have ascertained the current geometrical parameter values and illustrated the Universe’s accelerating behavior. Through the use of physical characteristics such as energy density, pressure, and equation of state parameter, we have talked about the physical behavior of the cosmos in our model. Additionally, we have looked at the kinematic parameters such as the jerk, deceleration, and Hubble parameters of the cosmos in our model. The deceleration parameter q(z) in our model represents the phase transition of the cosmos from deceleration to acceleration. Additionally, the deceleration parameter’s current value is
confidence bounds. It has been observed that the values obtained are all within the range that is indicated by cosmological observations. Through the utilization of the free parameter best-fit values, we have ascertained the current geometrical parameter values and illustrated the Universe’s accelerating behavior. Through the use of physical characteristics such as energy density, pressure, and equation of state parameter, we have talked about the physical behavior of the cosmos in our model. Additionally, we have looked at the kinematic parameters such as the jerk, deceleration, and Hubble parameters of the cosmos in our model. The deceleration parameter q(z) in our model represents the phase transition of the cosmos from deceleration to acceleration. Additionally, the deceleration parameter’s current value is 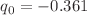 , and the transition redshift value is
, and the transition redshift value is 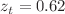 . This kind of situation is closely linked to the conventional
. This kind of situation is closely linked to the conventional 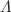 CDM model.
CDM model.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




