https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06100-x
Regular Article
Development of an epithermal and fast neutron target station for the High Brilliance Neutron Source
1
Jülich Centre for Neutron Science (JCNS-2), Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, Leo-Brandt Straße 1, 52428, Jülich, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany
2
Instituto Balseiro, Universidad Nacional de Cuyo, Av. Bustillo 9500, 8400, San Carlos de Bariloche, Río Negro, Argentina
3
University of Applied Sciences, FH Aachen, Bayernallee 9, 52066, Aachen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany
4
Neutron Physics Department, Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica (CNEA), Av. Bustillo 9500, 8500, San Carlos de Bariloche, Río Negro, Argentina
5
Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Buenos Aires, Argentina
Received:
29
August
2024
Accepted:
8
February
2025
Published online:
27
February
2025
The conceptual design of an epithermal and fast neutron target–moderator–reflector (TMR) unit for the High Brilliance Neutron Source (HBS) project is presented. A total of 450 simulations with the Monte Carlo code PHITS were analyzed to explore different combinations and thicknesses of pre-moderator and moderator materials. For each case, the highest epithermal outgoing neutron current at the end of an extraction channel was obtained. Analysis of the outgoing current density showed that the neutron spectra are independent of the proton pulse width, while the integral outgoing current is proportional to the pulse width, indicating a trade-off between the time resolution obtained and the neutron flux per pulse expected at the sample position. The neutron time distribution analysis showed that 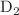 O as pre-moderator, combined with
O as pre-moderator, combined with 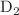 O, 7LiF or graphite as moderators, will provide a competitive epithermal neutron current. The averaged epithermal and fast values obtained for the 96 Hz station and 167
O, 7LiF or graphite as moderators, will provide a competitive epithermal neutron current. The averaged epithermal and fast values obtained for the 96 Hz station and 167 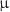 s proton pulse width are
s proton pulse width are  and
and 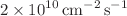 for the epithermal and fast neutron extraction channels, respectively, with reductions expected for short proton pulses in burst-mode operation.
for the epithermal and fast neutron extraction channels, respectively, with reductions expected for short proton pulses in burst-mode operation.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




