https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06024-6
Regular Article
Angular momentum dependence of nuclear decay of radon isotopes by emission of  C nuclei and branching ratio relative to
C nuclei and branching ratio relative to  -decay
-decay
1
The Research Centre of Nuclear Science and Technology (RCNST), Institute of Geological and Mining Research, P.O. Box 4110, Yaounde, Cameroon
2
Laboratory of Atomic, Molecular and Nuclear Physics, Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University of Yaounde I, P.O. Box 812, Yaounde, Cameroon
3
Centre for Atomic, Molecular Physics and Quantum Optics, University of Douala, P.O. Box 8580, Douala, Cameroon
Received:
23
October
2024
Accepted:
13
January
2025
Published online:
6
February
2025
This study aims to provide new insights into the angular momentum dependence of  C-decay. To achieve this, we perform a systematic analysis of the radioactive decay of radon isotopes via
C-decay. To achieve this, we perform a systematic analysis of the radioactive decay of radon isotopes via  C cluster emission, employing the Wentzel–Kramers–Brillouin approximation and introducing the screened Kratzer–Morse potential as an innovative nuclear potential. While the
C cluster emission, employing the Wentzel–Kramers–Brillouin approximation and introducing the screened Kratzer–Morse potential as an innovative nuclear potential. While the  C emission from radon isotopes has not yet been identified experimentally, our study extends the classical theory of
C emission from radon isotopes has not yet been identified experimentally, our study extends the classical theory of  -decay to predict half-lives and branching ratios for
-decay to predict half-lives and branching ratios for  C-decay in radon isotopes
C-decay in radon isotopes  Rn. The results of this work indicate that low angular momentum states favor
Rn. The results of this work indicate that low angular momentum states favor  C emission, and the predicted half-lives are consistent with previous theoretical studies. On the other hand, the calculation of branching ratio relative to
C emission, and the predicted half-lives are consistent with previous theoretical studies. On the other hand, the calculation of branching ratio relative to  decay allowed us to quantify the probability of
decay allowed us to quantify the probability of  C-decay channel for different values of l. The branching ratios suggest that radon isotopes belonging to the naturally occurring radioactive series are the most favorable regarding
C-decay channel for different values of l. The branching ratios suggest that radon isotopes belonging to the naturally occurring radioactive series are the most favorable regarding  C emission, especially the
C emission, especially the  Rn, which is prime candidate for potential experimental detection of
Rn, which is prime candidate for potential experimental detection of  C emission. Due to limited experimental data on
C emission. Due to limited experimental data on  C emission from radon isotopes, to validate our model we extended our calculations to other cluster decays with available half-lives, including
C emission from radon isotopes, to validate our model we extended our calculations to other cluster decays with available half-lives, including  C,
C,  O,
O,  Ne,
Ne, 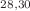 Mg, and
Mg, and 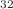 Si emissions from heavy nuclei. Our predicted half-lives values for cluster emission are validated by experimental data, especially for low angular momentum values.
Si emissions from heavy nuclei. Our predicted half-lives values for cluster emission are validated by experimental data, especially for low angular momentum values.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




