https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05321-w
Regular Article
Modulational instability and travelling waves in (2+1)-dimensional alpha-helix protein chains with diagonal and off-diagonal couplings
1
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University of Douala, P.O. Box 24157, Douala, Cameroon
2
Department of Physics and Geosciences, Faculty of Science, University of Bertoua, P.O. Box 416, Bertoua, Cameroon
3
Department of Wood and Forest Sciences, Higher Institute of Agriculture, Wood, Water Ressources, and Environment of Belabo, University of Bertoua, P.O. Box 60, Belabo, Cameroon
4
Laboratory of Biophysics, Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University of Yaounde I, P.O. Box 812, Yaoundé, Cameroon
5
Laboratory of Energy, Materials, Modeling and Methods(LE3M), National Higher Polytechnic school of Douala, University of Douala, P.O. Box 2701, Douala, Cameroon
6
African Centre for Advanced Studies, P.O. Box 4477, Yaoundé, Cameroon
7
Botswana International University of Science and Technology, Private Mail Bag 16, Palapye, Botswana
Received:
30
January
2024
Accepted:
28
May
2024
Published online:
11
June
2024
This paper examines the dynamics of a single-stranded alpha-helical protein chains in two dimensions. It establishes that the dynamics of such a system is governed by a two-dimensional continuous cubic-quintic nonlinear Schrödinger equation. With the use of modulational instability, linear stability analysis is performed. It appears that the amplitude of the growth rate and the number of regions of instability are affected by certain coupling parameters of the system such as diagonal and off-diagonal coupling constants. The new 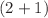 -extended direct algebraic method is applied to construct analytical solutions. Anti-kink, kink, dark and bright solitary waves are some results of propagating waves in the studied protein chains. Numerical simulations are performed to materialize these waves as stable.
-extended direct algebraic method is applied to construct analytical solutions. Anti-kink, kink, dark and bright solitary waves are some results of propagating waves in the studied protein chains. Numerical simulations are performed to materialize these waves as stable.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




