https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06025-5
Regular Article
Modeling scabies transmission dynamics: a stochastic approach with spectral collocation and neural network insights
1
School of Mathematics and Statistics, Central South University, 410083, Changsha, Hunan, China
2
Department of Mathematics, City University of Science and Information Technology, Peshawar, Pakistan
3
Department of Quantitative Analysis, College of Business Administration, King Saud University, P.O. Box 71115, 11587, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
4
Department of Nuclear and Renewable Energy, Ural Federal University Named After the First President of Russia Boris Yeltsin, 620002, Ekaterinburg, Russia
5
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Karpagam Academy of Higher Education, 641021, Coimbatore, India
6
Department of Technical Sciences, Western Caspian University, Baku, Azerbaijan
Received:
19
December
2024
Accepted:
13
January
2025
Published online:
24
January
2025
This research conducts a computational analysis of a stochastic scabies model using the Legendre spectral collocation technique (LSCM). By including stochasticity into the model via the suggested stochastic differential equations, we are confiscating the random fluctuations required for disease growth and spread. The stability, convergence, and accurate characteristics of the LSCM are meticulously examined, showcasing its efficacy in addressing complicated epidemiological problems. Furthermore, this mathematical model is used to explain the transmission dynamics of scabies infection in the population with standard incident rate. The dynamics of scabies are illustrated schematically, and then an ordinary differential equation (ODE) is derived using the law of mass action. Positiveness, boundedness, and equilibrium points have been analyzed. Next-generation techniques are used to determine the reproduction number. Sensitivity analysis is also accomplished to investigate the impact of various parameters of reproduction number. Disease-free equilibrium exists asymptotically in local whenever 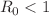 . The accuracy and effectiveness of the constructed stochastic computing using neural networks are shown by a comparison of the results derived from the dataset utilizing the spectral collocation approach. Our research demonstrates that mitigating the severe impacts of scabies requires prompt detection and timely intervention. Additionally, our mathematical model serves as a valuable tool for refining disease management strategies. This study enhances our understanding of scabies dynamics, offering actionable insights into public health planning and epidemic control.
. The accuracy and effectiveness of the constructed stochastic computing using neural networks are shown by a comparison of the results derived from the dataset utilizing the spectral collocation approach. Our research demonstrates that mitigating the severe impacts of scabies requires prompt detection and timely intervention. Additionally, our mathematical model serves as a valuable tool for refining disease management strategies. This study enhances our understanding of scabies dynamics, offering actionable insights into public health planning and epidemic control.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




