https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-05981-2
Regular Article
Transverse momentum spectra and angular correlations in  -hadron production in relativistic heavy-ion collisions
-hadron production in relativistic heavy-ion collisions
1
Key Laboratory of Quark and Lepton Physics (MOE) and Institute of Particle Physics, Central China Normal University, 430079, Wuhan, China
2
School of Science and Engineering, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, 518172, Shenzhen, China
3
University of Science and Technology of China, 230026, Hefei, Anhui, People’s Republic of China
4
Key Laboratory of Atomic and Subatomic Structure and Quantum Control (MOE), Guangdong Basic Research Center of Excellence for Structure and Fundamental Interactions of Matter, Institute of Quantum Matter, South China Normal University, 510006, Guangzhou, China
5
Guangdong-Hong Kong Joint Laboratory of Quantum Matter, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Nuclear Science, Southern Nuclear Science Computing Center, South China Normal University, 510006, Guangzhou, China
Received:
9
January
2024
Accepted:
3
January
2025
Published online:
23
January
2025
We carry out a detailed study of medium modifications on transverse momentum spectra and angular correlations between a large transverse momentum hadron and a  trigger in relativistic heavy-ion collisions within a perturbative QCD parton model improved by the Sudakov resummation technique. The total energy loss of a hard parton propagating inside the medium is employed to modify the fragmentation function, while the medium-induced transverse momentum broadening is included in the resummation approach, and both of them are related to the jet transport parameter and obtained by the higher-twist formalism. We obtain good agreements with the existing data on transverse momentum and azimuthal angular correlations for the
trigger in relativistic heavy-ion collisions within a perturbative QCD parton model improved by the Sudakov resummation technique. The total energy loss of a hard parton propagating inside the medium is employed to modify the fragmentation function, while the medium-induced transverse momentum broadening is included in the resummation approach, and both of them are related to the jet transport parameter and obtained by the higher-twist formalism. We obtain good agreements with the existing data on transverse momentum and azimuthal angular correlations for the  -hadron pairs in pp and AA collisions and predict the correlations for the
-hadron pairs in pp and AA collisions and predict the correlations for the 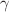 -hadron in central PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV. The numerical analyses for the
-hadron in central PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV. The numerical analyses for the  -hadron in central PbPb collisions show that the normalized angular distribution is decorrelated due to the medium-induced transverse momentum broadening; however, the angular correlation is enhanced due to the parton energy loss, namely anti-broadening. The observed modification of the angular correlation is a result of the competition between the broadening and the anti-broadening. This work provides a reliable theoretical tool for a comprehensive and precise study of jet quenching in relativistic heavy-ion collisions.
-hadron in central PbPb collisions show that the normalized angular distribution is decorrelated due to the medium-induced transverse momentum broadening; however, the angular correlation is enhanced due to the parton energy loss, namely anti-broadening. The observed modification of the angular correlation is a result of the competition between the broadening and the anti-broadening. This work provides a reliable theoretical tool for a comprehensive and precise study of jet quenching in relativistic heavy-ion collisions.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




