https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-05971-4
Regular Article
Emulating cyclone Roanus interaction with tide and surge through the method of lines: a numerical analysis
1
Mathematics Discipline, Khulna University, 9208, Khulna, Bangladesh
2
Department of Mathematics, University of Rajshahi, 6205, Rajshahi, Bangladesh
Received:
10
July
2024
Accepted:
2
January
2025
Published online:
15
January
2025
The shallow water equations were developed to predict changes in water levels resulting from the nonlinear tide-surge interaction associated with cyclonic storm Roanu, which impacted the east coast of Bangladesh. To solve these equations, the numerical method of lines was used in coordination with the Runge–Kutta (4,4) technique. A five-point central difference approximation was employed to discretize the spatial partial derivatives of the shallow water equations, resulting in a system of ordinary differential equations in time, which were then solved using the Runge–Kutta (4,4) method. The stair-step approach was utilized to model the land-sea interface, capturing key coastal features, including land and river dynamics, with special emphasis on the Meghna River’s freshwater runoff. To simulate tidal cycles and achieve stable tidal conditions, tidal forcing was applied along the southern open boundary of the model using four major tidal constituents: 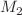 (principal lunar semidiurnal),
(principal lunar semidiurnal), 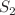 (principal solar semidiurnal),
(principal solar semidiurnal),  (lunisolar diurnal), and
(lunisolar diurnal), and 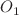 (principal lunar diurnal) along the southern open boundary of the model. The simulated water levels due to the nonlinear tide-surge interaction closely matched observations from the Bangladesh Inland Water Transport Authority and were deemed reliable based on the root mean square error values.
(principal lunar diurnal) along the southern open boundary of the model. The simulated water levels due to the nonlinear tide-surge interaction closely matched observations from the Bangladesh Inland Water Transport Authority and were deemed reliable based on the root mean square error values.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




