https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05767-y
Regular Article
Energy distribution in long-range-interacting weighted geographic networks
1
Departamento de Física Teórica e Experimental, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Campus Universitário, 59072-970, Natal, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil
2
Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal do Ceará, 60451-970, Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil
3
National Institute of Science and Technology of Complex Systems, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
4
Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas, Rua Dr. Xavier Sigaud 150, 22290-180, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
5
Santa Fe Institute, 1399 Hyde Park Road, 87501, Santa Fe, USA
6
Complexity Science Hub Vienna, Josefstadter Strasse 39, 1080, Vienna, Austria
Received:
29
July
2024
Accepted:
22
October
2024
Published online:
6
November
2024
We numerically investigate a geographical d-dimensional (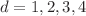 ) Bianconi–Barabási-like model, characterized by preferential attachment growth mechanisms influenced by Euclidean distances and weighted edges. The weights of the edges follow a predetermined random probability distribution. This model is implemented through a straightforward energy-driven dynamics and exhibits the distribution of ’energy’ per site in its quasi-stationary state. Across all networks generated by this model, we observe q-exponential energy distributions over the entire parameter space, which exhibits that this model belongs to the realm of nonadditive q-entropies. Additionally, the time evolution of the site energies, characterized by the dynamic
) Bianconi–Barabási-like model, characterized by preferential attachment growth mechanisms influenced by Euclidean distances and weighted edges. The weights of the edges follow a predetermined random probability distribution. This model is implemented through a straightforward energy-driven dynamics and exhibits the distribution of ’energy’ per site in its quasi-stationary state. Across all networks generated by this model, we observe q-exponential energy distributions over the entire parameter space, which exhibits that this model belongs to the realm of nonadditive q-entropies. Additionally, the time evolution of the site energies, characterized by the dynamic 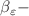 exponent, is analyzed.
exponent, is analyzed.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




