https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05675-1
Regular Article
Comparative analysis of heat transfer studies on a tilted porous rectangular enclosure filled with nanofluids by considering the impacts of the magnetic field and heat sink or source
1
Department of Mathematics, School of Advanced Sciences, Vellore Institute of Technology, 632014, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Mathematics and Statistics, School of Applied Sciences and Humanities, Vignan’s Foundation for Science, Technology and Research, 522213, Vadlamudi, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India
3
Department of Mathematics and Computing, Dr B. R. Ambedkar National Institute of Technology, 144027, Jalandhar, Punjab, India
Received:
1
July
2024
Accepted:
16
September
2024
Published online:
2
October
2024
Analysing the fluid flow and heat transfer of the inclined rectangular cavity filled with Aluminium Oxide 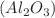 /Iron Oxide
/Iron Oxide 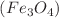 -water nanofluid is the main objective of this study. The study of these nanofluids has immensely improved, and determinations exhibit that these fluids are significantly heat transfer fluids for numerous industrial sectors such as electronics, manufacturing, automotive, and construction and building. The left and right walls of the cavity is uniformly heated and cooled, respectively. The cavity’s top and bottom walls are partly heated and cooled; other portions are adiabatic. The Marker-And-Cell technique and the finite difference methodology are employed to examine the pertinent parameters: Hartmann number (Ha), Darcy number (Da), nanoparticles volume fraction
-water nanofluid is the main objective of this study. The study of these nanofluids has immensely improved, and determinations exhibit that these fluids are significantly heat transfer fluids for numerous industrial sectors such as electronics, manufacturing, automotive, and construction and building. The left and right walls of the cavity is uniformly heated and cooled, respectively. The cavity’s top and bottom walls are partly heated and cooled; other portions are adiabatic. The Marker-And-Cell technique and the finite difference methodology are employed to examine the pertinent parameters: Hartmann number (Ha), Darcy number (Da), nanoparticles volume fraction 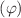 , heat sink or source (Q), and inclination angle of the cavity
, heat sink or source (Q), and inclination angle of the cavity  . Results are graphically visualized with isotherms, streamlines, and average and local Nusselt numbers. In comparison with
. Results are graphically visualized with isotherms, streamlines, and average and local Nusselt numbers. In comparison with 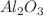 -water nanofluid and
-water nanofluid and  -water nanofluid with
-water nanofluid with 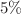 of nanoparticles, the
of nanoparticles, the  -water nanofluid improves the transfer of heat by
-water nanofluid improves the transfer of heat by 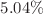 . In terms of flow of fluid, transfer of heat, and local and average heat transference rate,
. In terms of flow of fluid, transfer of heat, and local and average heat transference rate,  -water nanofluid performs better than
-water nanofluid performs better than 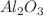 -water nanofluid.
-water nanofluid.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




