https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05431-5
Regular Article
A general formulation of the Gibbs free energy regarding six linear symmetric triatomic species
1
School of Sciences, Southwest Petroleum University, 610500, Chengdu, China
2
National Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation, Southwest Petroleum University, 610500, Chengdu, China
3
School of Physics Science and Engineering, Tongji University, 200092, Shanghai, China
4
School of Mechanical Engineering, Sichuan University of Science & Engineering, 644005, Yibin, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China
5
Research Institute of Tianfu New Energy, 610041, Chengdu, China
a
1761088695@qq.com
h
chshjia@263.net
Received:
18
June
2024
Accepted:
5
July
2024
Published online:
26
July
2024
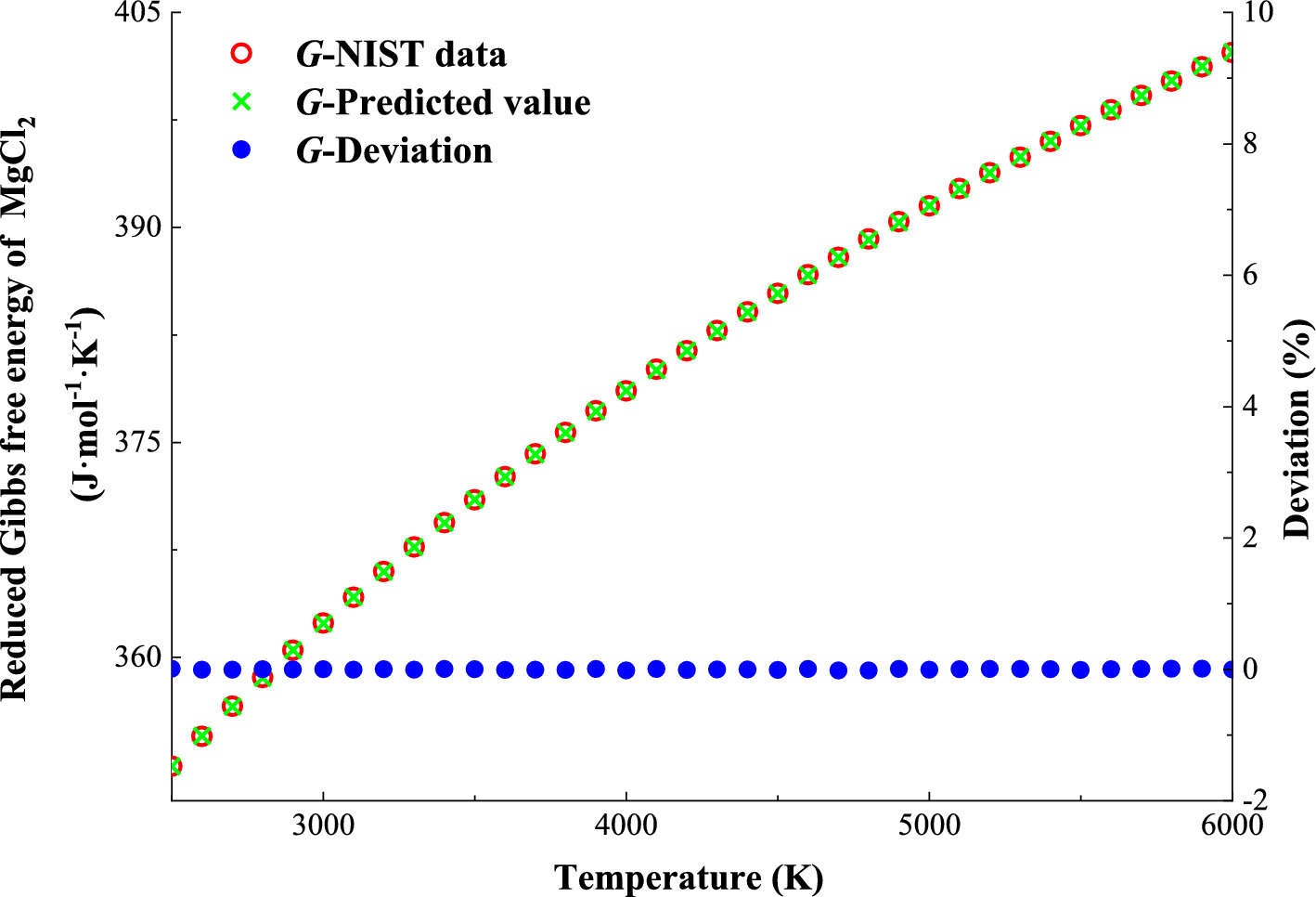
We develop a general formulation of the Gibbs free energy for six linear symmetric triatomic species. The established formulation representation only correlates masses of atoms, standard experimental values of five molecular constants and an adjustable dimensionless pure number, whereas the conventional functional correlations involve multiple adjustable coefficients determined through fitting plenty of experimental data, and those coefficients have different values regarding different species. The mean relative errors between the predicted values from the proposed prediction models and the NIST data subject to six triatomic species regarding the Gibbs free energy, entropy, enthalpy, and isobaric heat capacity are within the ranges of 0.006% to 0.053%, 0.020% to 0.132%, 0.220% to 1.378%, and 0.640% to 1.334%, respectively. The developed general Gibbs free energy prediction model has the high reliability.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.