https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05315-8
Regular Article
Modeling the interplay in spatiotemporal dynamics of calcium, 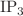 , and phospholipase C-
, and phospholipase C-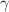 l in a fibroblast cell
l in a fibroblast cell
DoM, S. V. National Institute of Technology, 395007, Surat, Gujarat, India
Received:
8
April
2024
Accepted:
24
May
2024
Published online:
14
June
2024
The interconnected bioenergetic processes involving calcium (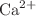 ), inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphophate (
), inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphophate (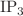 ), and phospholipase C-
), and phospholipase C-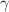 l (
l (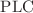 ) play a crucial role in regulating various mechanisms within the fibroblast. Disruptions in the dynamics of calcium,
) play a crucial role in regulating various mechanisms within the fibroblast. Disruptions in the dynamics of calcium, 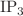 , or
, or 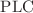 can lead to toxicity and cell death. While some studies have investigated the interactions between calcium and either
can lead to toxicity and cell death. While some studies have investigated the interactions between calcium and either 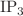 and
and 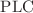 individually, limited insights have been gained into the regulatory and dysregulatory processes within fibroblast cells. Moreover, there is a lack of research on the interplay among all three systems:
individually, limited insights have been gained into the regulatory and dysregulatory processes within fibroblast cells. Moreover, there is a lack of research on the interplay among all three systems: 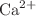 ,
, 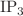 , and
, and 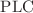 . To address this gap, a mathematical model was developed to study the cross-talk among these systems. The model incorporates two-way feedback processes between
. To address this gap, a mathematical model was developed to study the cross-talk among these systems. The model incorporates two-way feedback processes between 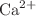 and
and 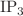 , as well as between
, as well as between 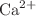 and
and 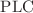 , facilitated by
, facilitated by 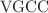 and plasmalemmal
and plasmalemmal 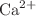 -ATPase (
-ATPase (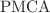 ). This coupling mechanism automatically accounts for the indirect two-way feedback between
). This coupling mechanism automatically accounts for the indirect two-way feedback between 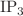 and
and 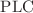 . Numerical simulations, performed using the
. Numerical simulations, performed using the 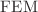 with the Crank–Nicolson scheme (CNS), revealed novel insights into the regulatory and dysregulatory processes involving various factors such as buffers and
with the Crank–Nicolson scheme (CNS), revealed novel insights into the regulatory and dysregulatory processes involving various factors such as buffers and 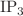 receptors through the
receptors through the 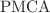 pump. The model, which also considers the buffer,
pump. The model, which also considers the buffer, 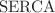 pump, and
pump, and 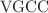 , sheds light on the interactive spatiotemporal dynamics of
, sheds light on the interactive spatiotemporal dynamics of 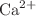 ,
, 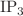 , and
, and 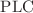 in fibroblast. Importantly, the study highlights that the behavior of crucial mechanisms differs significantly between interactions involving two systems
in fibroblast. Importantly, the study highlights that the behavior of crucial mechanisms differs significantly between interactions involving two systems 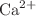 and
and 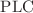 and those involving all three systems
and those involving all three systems 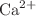 ,
, 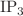 , and
, and 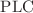 , owing to mutual regulatory adjustments. The research also explores the association between alterations in
, owing to mutual regulatory adjustments. The research also explores the association between alterations in 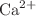 ,
, 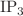 , and
, and 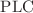 dynamics and various fibrotic disorders in fibroblasts.
dynamics and various fibrotic disorders in fibroblasts.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




