https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05215-x
Regular Article
Reflection and transmission of plane waves from the interface of a porothermoelastic solid and a double porosity solid
Department of Mathematics, Maharshi Dayanand University, 124001, Rohtak, Haryana, India
Received:
23
April
2024
Accepted:
24
April
2024
Published online:
2
June
2024
In this study, we analyze the reflection and refraction of a homogeneous plane-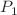 -wave at the interface between a porothermoelastic solid medium and a double porosity medium. The incidence of the
-wave at the interface between a porothermoelastic solid medium and a double porosity medium. The incidence of the 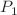 wave generates four reflected waves in porothermoelastic media and four transmitted waves in double porosity media. Generalized governing equations for the double porosity medium are solved via potential functions, predicting one shear and three dilatational waves. For the porothermoelastic medium, motion equations are solved using plane wave solutions. The computation of theoretical expressions for reflection and transmission coefficients involves a system of eight non-homogeneous linear equations, based on boundary constraints. The findings demonstrate a significant influence of incidence angle on the amplitude ratios of each reflected and refracted wave. Mathematical derivations explore the impact of material parameters of porothermoelastic medium (porosity, linear and volumetric thermal expansion coefficients, and tortuosity), and double porosity medium (total porosity, volume fraction of fractured pores, and matrix porosity) on amplitude ratios of waves. Propagation characteristics for different boundary constraints (permeable/impermeable, and thermally insulated/isothermal) are numerically compared. In addition, variations of velocities of all reflected and transmitted waves with different frequencies are represented graphically.
wave generates four reflected waves in porothermoelastic media and four transmitted waves in double porosity media. Generalized governing equations for the double porosity medium are solved via potential functions, predicting one shear and three dilatational waves. For the porothermoelastic medium, motion equations are solved using plane wave solutions. The computation of theoretical expressions for reflection and transmission coefficients involves a system of eight non-homogeneous linear equations, based on boundary constraints. The findings demonstrate a significant influence of incidence angle on the amplitude ratios of each reflected and refracted wave. Mathematical derivations explore the impact of material parameters of porothermoelastic medium (porosity, linear and volumetric thermal expansion coefficients, and tortuosity), and double porosity medium (total porosity, volume fraction of fractured pores, and matrix porosity) on amplitude ratios of waves. Propagation characteristics for different boundary constraints (permeable/impermeable, and thermally insulated/isothermal) are numerically compared. In addition, variations of velocities of all reflected and transmitted waves with different frequencies are represented graphically.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




