https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05259-z
Regular Article
Exact perfect fluid interior solutions and slowly rotating relativistic stars
1
School of Mathematical Sciences, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua, Zhejiang, China
2
Department of Mathematics, University of Management and Technology, Sialkot Campus, Lahore, Pakistan
3
School of Computing and Mathematical Sciences, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK
b mfs24@leicester.ac.uk, farasat.shamir@gmai.com
Received:
4
March
2024
Accepted:
7
May
2024
Published online:
28
May
2024
The purpose of this paper is two fold. The first part of the paper is devoted to investigate some exact perfect fluid interior solutions. For this purpose, we propose the metric coefficient 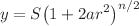 , where a and S are arbitrary constants to be determined from the matching conditions and n is an odd positive integer. In particular, we construct the exact solutions for the case
, where a and S are arbitrary constants to be determined from the matching conditions and n is an odd positive integer. In particular, we construct the exact solutions for the case 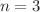 . Some important physical analysis is provided by considering the compact structures similar to those having radius
. Some important physical analysis is provided by considering the compact structures similar to those having radius 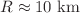 . We choose some light stars with a mass around
. We choose some light stars with a mass around  , stars with an intermediate mass around
, stars with an intermediate mass around 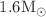 and some heavy stars with a mass around
and some heavy stars with a mass around 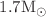 . A qualitative analysis is done to find the acceptability of exact solutions. The pressure and density profiles are positive and monotonically decreasing with maximum values at the center. Further, the energy conditions are also satisfied. The causality condition is also obeyed and the adiabatic index is also found to be in the acceptable range. The second part of the paper focuses on discussing the dynamics of rotating stars. A modified spacetime including the effects of angular velocity has been used to find the moment of inertia of rotating stars. Some suitable numerical values are assumed for the involved parameters to get the masses and radii of stars with in our targeted range. In particular, neutron stars are obtained with radii
. A qualitative analysis is done to find the acceptability of exact solutions. The pressure and density profiles are positive and monotonically decreasing with maximum values at the center. Further, the energy conditions are also satisfied. The causality condition is also obeyed and the adiabatic index is also found to be in the acceptable range. The second part of the paper focuses on discussing the dynamics of rotating stars. A modified spacetime including the effects of angular velocity has been used to find the moment of inertia of rotating stars. Some suitable numerical values are assumed for the involved parameters to get the masses and radii of stars with in our targeted range. In particular, neutron stars are obtained with radii 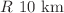 and masses up to
and masses up to 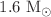 . The behavior of moment of inertia of the sphere against the solar mass is investigated and it is found that moment of inertia increases with an increase in solar mass. Also, the relationships of mass and energy density against the radius of the compact structure show quite natural behavior and show the acceptability of our analysis. In particular, the current study supports the existence of realistic structures like LMC X-4 and 4U 1820-30.
. The behavior of moment of inertia of the sphere against the solar mass is investigated and it is found that moment of inertia increases with an increase in solar mass. Also, the relationships of mass and energy density against the radius of the compact structure show quite natural behavior and show the acceptability of our analysis. In particular, the current study supports the existence of realistic structures like LMC X-4 and 4U 1820-30.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




