https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05210-2
Regular Article
Magnetic impacts on double diffusion inside a porous NEPCM-filled annulus by a hybrid artificial intelligence and meshless simulations
1
Central Labs, King Khalid University, AlQura’a, Abha, P.O. Box 960, 62529, Abha, Saudi Arabia
2
Mathematics Department, Faculty of Science and Arts in Almakhwah, Al-Baha University, Al-Baha, Saudi Arabia
3
Department of Mathematics, College of Science, King Khalid University, 62529, Abha, Saudi Arabia
4
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, South Valley University, 83523, Qena, Egypt
Received:
1
December
2023
Accepted:
24
April
2024
Published online:
28
May
2024
The incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics (ISPH) approach was used in computational research to investigate the magnetic effects on thermosolutal convection of nano-encapsulated phase change material inside a porous annulus. The annulus is formed between two ellipses and consists of two circular cylinders. The ISPH approach is used to solve partial differential governing equations that have fractional time derivatives. This work applied the effects of thermo-diffusion and diffusion-thermo, fractional time derivative, Darcy number, Hartmann number, Rayleigh number, nanoparticles parameter, and inner cylinder radius on the isotherms 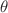 , isoconcentration
, isoconcentration  , a heat capacity ratio
, a heat capacity ratio 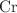 , and velocity field
, and velocity field 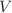 . This study found that the fractional time-derivative parameter serves as a dynamical time step, accelerating transient processes. Because of the porous media presence, a decrease in Darcy’s number lowers the velocity of the nanofluid within a porous annulus. The Rayleigh number and the size of the implanted circular cylinders influence the intensity of heat and mass transfer. The Soret number supports the distribution of isoconcentration and accelerates the nanofluid’s velocity. The mean Nusselt/Sherwood numbers
. This study found that the fractional time-derivative parameter serves as a dynamical time step, accelerating transient processes. Because of the porous media presence, a decrease in Darcy’s number lowers the velocity of the nanofluid within a porous annulus. The Rayleigh number and the size of the implanted circular cylinders influence the intensity of heat and mass transfer. The Soret number supports the distribution of isoconcentration and accelerates the nanofluid’s velocity. The mean Nusselt/Sherwood numbers 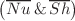 are changed by alterations in relevant factors. An artificial neural network (ANN) model is adopted to predict the values of
are changed by alterations in relevant factors. An artificial neural network (ANN) model is adopted to predict the values of 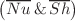 . The ANN model was shown to be a reliable method for anticipating the required values.
. The ANN model was shown to be a reliable method for anticipating the required values.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




