https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04289-3
Regular Article
Effects of dual rotations of two circular cylinders on thermosolutal convection of a nanofluid mobilized by a heterogeneous porous cavity
1
Department of Mathematics, College of Science, King Khalid University, P.O. Box 9004, 61413, Abha, Saudi Arabia
2
Department of Mathematical Sciences, College of Science, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, P.O. Box 84428, 11671, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
a
abdelreheam.abdallah@sci.svu.edu.eg
Received:
7
September
2022
Accepted:
15
July
2023
Published online:
2
August
2023
The thermosolutal convection of circular rotation of dual circular cylinders inside a combined cavity of a circular cylinder on a rectangular shape is numerically simulated by the ISPH method. The combined cavity is occupied by a nanofluid and porous media. Two levels of heterogeneous and homogeneous porous media are considered. The pertinent factors are scaled by nanoparticles parameter 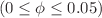 , levels of porous media
, levels of porous media  , Darcy parameter (
, Darcy parameter ( ), buoyancy parameter
), buoyancy parameter  , Rayleigh number (
, Rayleigh number ( ), and Lewis number
), and Lewis number  . The connections among the circular rotation of solid cylinders containing nanofluid plus porous media are modeled by the ISPH method. The main findings demonstrated that combining nanoparticles to
. The connections among the circular rotation of solid cylinders containing nanofluid plus porous media are modeled by the ISPH method. The main findings demonstrated that combining nanoparticles to 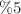 declines the nanofluid velocity due to extra viscosity. Increasing the buoyancy parameter accelerates the nanofluid movements and enhances the mean Nusselt number
declines the nanofluid velocity due to extra viscosity. Increasing the buoyancy parameter accelerates the nanofluid movements and enhances the mean Nusselt number 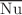 . The variations of porous levels are changing the nanofluid flow and characteristics of heat and mass transfer within a combined cavity. Rayleigh numbers play a significant job in enhancing the nanofluid velocity and thermosolutal convection in a combined cavity.
. The variations of porous levels are changing the nanofluid flow and characteristics of heat and mass transfer within a combined cavity. Rayleigh numbers play a significant job in enhancing the nanofluid velocity and thermosolutal convection in a combined cavity.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




