https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05163-6
Regular Article
Diagnostic and comparative analysis of dark energy models with q(z) parametrizations
1
Pacif Institute of Cosmology and Selfology (PICS), 768224, Sagara, Sambalpur, Odisha, India
2
Department of Applied Mathematics, Delhi Technological University, 110042, Delhi, India
3
Department of Physics, Zhejiang Normal University, 321004, Jinhua, People’s Republic of China
Received:
2
September
2023
Accepted:
5
April
2024
Published online:
2
May
2024
This manuscript presents a diagnostic analysis of three dark energy models resulting from the parametrization of the deceleration parameter. These models exhibit intriguing features, including late-time acceleration and a cosmological phase transition from early deceleration to late acceleration. The analysis utilizes parametrizations of the deceleration parameter, q(z), and employs Cosmic Chronometers (CC), Type Ia supernovae (SNIa), Gamma Ray Bursts (GRB), Quasar (Q) and Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) datasets to constrain the models and determine the best-fitting values of the model parameters. Additionally, the evolution of kinematic cosmographic parameters is investigated. The study focuses on discussing the statefinder and Om diagnostic analyses of the considered models, comparing them with the well-established 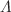 CDM and SCDM models. By utilizing information criteria, the viability of the models is examined, assessing their goodness of fit and their ability to explain the observed data. The results provide valuable insights into the behavior and characteristics of the dark energy models. The comparison with the standard models sheds light on the similarities and differences; while, the information criteria analysis offers a quantitative assessment of their suitability. This analysis contributes to our understanding of the dynamics and evolution of the Universe, furthering our knowledge of dark energy and its role in shaping the cosmos.
CDM and SCDM models. By utilizing information criteria, the viability of the models is examined, assessing their goodness of fit and their ability to explain the observed data. The results provide valuable insights into the behavior and characteristics of the dark energy models. The comparison with the standard models sheds light on the similarities and differences; while, the information criteria analysis offers a quantitative assessment of their suitability. This analysis contributes to our understanding of the dynamics and evolution of the Universe, furthering our knowledge of dark energy and its role in shaping the cosmos.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




