https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05112-3
Regular Article
Sheath structure behavior in collisional non-extensive plasma with negative ions
1
MASI Laboratory, Polydisciplinary Faculty of Nador, Mohammed First University, Nador, Morocco
2
Laboratory of Physics of Matter and Radiations, Faculty of Sciences, Mohammed First University, Oujda, Morocco
Received:
8
December
2023
Accepted:
18
March
2024
Published online:
3
May
2024
The present paper numerically investigates the sheath structure in a collisional electronegative plasma in the presence of non-zero ion source term. The plasma sheath contains non-extensively distributed electrons, fluid positive ions with finite temperature, and Boltzmann-distributed negative ions. Using the Sagdeev potential method, a modified Bohm sheath criterion is derived to obtain the ion velocity at the sheath entrance that satisfies the sheath formation condition. The impact of the main parameters like electronegativity D, non-extensivity q, ionization frequency  and collision frequency
and collision frequency 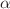 on the sheath characteristics has been examined. The requirement of positive ion velocity to enter the sheath is found to decrease with the increment of
on the sheath characteristics has been examined. The requirement of positive ion velocity to enter the sheath is found to decrease with the increment of 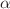 and
and  . Moreover, it is seen that as q, D,
. Moreover, it is seen that as q, D,  and
and 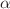 increase, the normalized electric potential rapidly rises, the peak amplitude of the space charge density increases, and the sheath thickness significantly decreases. Furthermore, as D decreases, the effect of q,
increase, the normalized electric potential rapidly rises, the peak amplitude of the space charge density increases, and the sheath thickness significantly decreases. Furthermore, as D decreases, the effect of q,  and
and 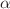 on the sheath electric potential and the space charge density becomes more important. This study may be useful in various technological applications, including plasma-based surface treatments, plasma etching, and plasma cleaning. This is particularly relevant in the microelectronic and semiconductor industries for manufacturing electronic devices and integrated circuits. Additionally, it could contribute to the enhancement and advancement of techniques in fusion energy research.
on the sheath electric potential and the space charge density becomes more important. This study may be useful in various technological applications, including plasma-based surface treatments, plasma etching, and plasma cleaning. This is particularly relevant in the microelectronic and semiconductor industries for manufacturing electronic devices and integrated circuits. Additionally, it could contribute to the enhancement and advancement of techniques in fusion energy research.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




