https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-04997-4
Regular Article
Examining the impact of incentives and vaccination on COVID-19 control in India: addressing environmental contamination and seasonal dynamics
1
Department of Basic Science and Humanities, Indian Institute of Information Technology, 813210, Bhagalpur, India
2
Department of Mathematics, University of Kalyani, Nadia, 741235, Kalyani, India
3
Department of Mathematics, Thapar Institute of Engineering & Technology, 147004, Patiala, India
Received:
20
November
2023
Accepted:
12
February
2024
Published online:
6
March
2024
In the present study, we explore the dynamics of COVID-19 by considering its spread through direct contacts of susceptibles with the infected ones and also via the contamination present in the environment. The model incorporates various factors such as recovery, awareness dissemination through media, precautionary measures, sanitation coverage, public health campaigns, vaccination and incentives provided by the government for the control of COVID-19. The basic reproduction number (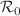 ) is calculated, which serves as an indicator of epidemic severity. We fitted our model by integrating real COVID-19 data from India and determined essential epidemiological parameters through estimation. The results from the sensitivity analysis emphasize the importance of reducing (enhancing) the values of parameters with positive (negative) indices to hinder the disease transmission. Further, we explore some optimal control strategies and their effectiveness in managing the disease spread, highlighting the significance of incentives in reducing the direct contacts, propagating awareness, and vaccination coverage. Moreover, we reveal the presence of bifurcations in the system that induce periodicity in the disease prevalence due to the seasonal variations in the concentration of environmental contamination and the rate of disease transmission. Overall, the findings suggest that the proposed control measures with optimum values can significantly contribute to the disease management, reducing its prevalence in the community. Additionally, our results suggest for the implementation of proper vaccination and sanitation coverages through awareness campaigns in order to eradicate the prevalence of COVID-19 in India.
) is calculated, which serves as an indicator of epidemic severity. We fitted our model by integrating real COVID-19 data from India and determined essential epidemiological parameters through estimation. The results from the sensitivity analysis emphasize the importance of reducing (enhancing) the values of parameters with positive (negative) indices to hinder the disease transmission. Further, we explore some optimal control strategies and their effectiveness in managing the disease spread, highlighting the significance of incentives in reducing the direct contacts, propagating awareness, and vaccination coverage. Moreover, we reveal the presence of bifurcations in the system that induce periodicity in the disease prevalence due to the seasonal variations in the concentration of environmental contamination and the rate of disease transmission. Overall, the findings suggest that the proposed control measures with optimum values can significantly contribute to the disease management, reducing its prevalence in the community. Additionally, our results suggest for the implementation of proper vaccination and sanitation coverages through awareness campaigns in order to eradicate the prevalence of COVID-19 in India.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




