https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-04949-y
Regular Article
Analysis of Caputo–Katugampola fractional differential system
School of Mathematics, Hefei University of Technology, 230601, Hefei, China
Received:
8
January
2024
Accepted:
26
January
2024
Published online:
16
February
2024
In this paper, we propose the approach of 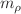 -Laplace transform and implement it to the stability of Caputo–Katugampola fractional differential system (CKFDS). First, the sufficient condition of existence of
-Laplace transform and implement it to the stability of Caputo–Katugampola fractional differential system (CKFDS). First, the sufficient condition of existence of 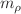 -Laplace transform and the well-posedness of the inverse
-Laplace transform and the well-posedness of the inverse 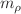 -Laplace transform are clarified, respectively. In addition, some properties of
-Laplace transform are clarified, respectively. In addition, some properties of 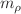 -Laplace transform, including Katugampola fractional calculus and the corresponding differential system, are also presented. Then, in view of
-Laplace transform, including Katugampola fractional calculus and the corresponding differential system, are also presented. Then, in view of 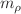 -Laplace transform, the stability criteria of solutions to linear CKFDS with and without delay are analysed, respectively. Not only that, in light of the observation of decay rate of solution to linear CKFDS, a novel inverse power-logarithmic law is thus obtained as a bridge between the classical inverse power law and the inverse logarithmic law. Finally, to verify the reliability and validity of the proposed approach, some necessary illustrations are given and analysed in detail. Such modified integral transform serves as a potent tool for effectively handling generalized fractional operators with specialized kernels as Katugampola fractional calculus. Furthermore, the CKFDS encompasses a compound inverse power-logarithmic law with specific physical significance, making it indispensable in elucidating anomalous dynamic evolution, particularly in ultra-slow varying processes characterized by long memory and heredity.
-Laplace transform, the stability criteria of solutions to linear CKFDS with and without delay are analysed, respectively. Not only that, in light of the observation of decay rate of solution to linear CKFDS, a novel inverse power-logarithmic law is thus obtained as a bridge between the classical inverse power law and the inverse logarithmic law. Finally, to verify the reliability and validity of the proposed approach, some necessary illustrations are given and analysed in detail. Such modified integral transform serves as a potent tool for effectively handling generalized fractional operators with specialized kernels as Katugampola fractional calculus. Furthermore, the CKFDS encompasses a compound inverse power-logarithmic law with specific physical significance, making it indispensable in elucidating anomalous dynamic evolution, particularly in ultra-slow varying processes characterized by long memory and heredity.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




