https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04634-6
Regular Article
Effect of vaccination rate in multi-wave compartmental model
1
Department of Physics, Centre for Nonlinear Science and Engineering, School of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, SASTRA University, 613 401, Thanjavur, India
2
School of Physics, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, 695016, Thiruvananthapuram, India
d
skumarusnld@gmail.com
e
chandru25nld@gmail.com
Received:
8
August
2023
Accepted:
26
October
2023
Published online:
8
November
2023
We present a mathematical model to explore the dynamics of infectious diseases with multiple waves of infection. First, an analysis of the isolated community with multi-wave dynamics is considered. We find that the isolated community reaches disease-free equilibrium state from multi-wave state via endemic equilibrium. In addition to these states, the two-patch community facilitates the onset of birhythmicity, multi-stable states and heterogeneous endemic state for suitable parameter choices. We find that the dynamical transitions are mediated by Hopf bifurcation, transcritical bifurcation and saddle-node bifurcation on limit cycle. Specifically, we elucidate the interplay of the dispersal strength, the mean-field strength and the vaccination rate on the dynamics of the infected compartmental classes of the interconnected communities and identified the suitable ranges of these parameters to achieve disease-free equilibrium state. We also deduce the basic reproduction number (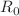 ) using the framework of the next-generation matrix, which corroborates the stability of the endemic and disease-free equilibriums.
) using the framework of the next-generation matrix, which corroborates the stability of the endemic and disease-free equilibriums.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




