https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04589-8
Regular Article
Dynamical behaviors and event-triggered impulsive control of a delayed information propagation model based on public sentiment and forced silence
1
School of Economics, Northeastern University at Qinhuangdao, 066004, Qinhuangdao, Hebei, China
2
School of Management, Northeastern University at Qinhuangdao, 066004, Qinhuangdao, Hebei, China
3
School of Business Administration, Northeastern University, 110819, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Received:
31
July
2023
Accepted:
10
October
2023
Published online:
4
November
2023
Adverse information can spread through emotional expression to cause public panic and social instability. The network regulators may limit the spread by force silently. This paper aims to capture the effects of public sentiment and forced silence on information propagation. To this end, the paper proposes a class of SFPFNR information propagation models with time delays and a forced silence function on a heterogeneous network. In addition, event-triggered impulsive control mechanism is designed. Combined with forced silence, the paper creates a dual control mechanism. Next, the mean-field principle is used to calculate the basic reproduction number 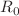 and then prove the existence of the equilibrium point
and then prove the existence of the equilibrium point 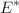 . By constructing the Lyapunov function and applying the comparison principle, the global and local stability of the system are then discussed. Besides, we perform extensive numerical simulations to verify the theoretical conclusions. The results show that time delays do not affect system stability, and negative emotions are crucial for large-scale information transmission. Finally, the model is applied to the actual case and shows a significant improvement in prediction accuracy compared with the SIR model. The RMSE decreases from 0.3234 to 0.0664. Therefore, the model can guide social media management and information dissemination regulation.
. By constructing the Lyapunov function and applying the comparison principle, the global and local stability of the system are then discussed. Besides, we perform extensive numerical simulations to verify the theoretical conclusions. The results show that time delays do not affect system stability, and negative emotions are crucial for large-scale information transmission. Finally, the model is applied to the actual case and shows a significant improvement in prediction accuracy compared with the SIR model. The RMSE decreases from 0.3234 to 0.0664. Therefore, the model can guide social media management and information dissemination regulation.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.





