https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04417-z
Regular Article
Analysis of complexity factor for charged dissipative configuration in modified gravity
1
Department of Mathematics and Statistics, The University of Lahore, 1-KM Defence Road, Lahore, Pakistan
2
Department of Mathematics, University of the Punjab, Quaid-e-Azam Campus, 54590, Lahore, Pakistan
Received:
6
April
2023
Accepted:
24
August
2023
Published online:
5
September
2023
In this paper, we determine the electromagnetic effects on the complexity factor of radiating anisotropic cylindrical geometry in the background of 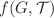 theory. The self-gravitating objects possessing inhomogeneous energy density, pressure anisotropy, heat flux, charge and correction terms appear to encounter the complexity producing phase. Herrera’s orthogonal splitting method is used to identify the scalar functions in which the factor that incorporates all of the fundamental aspects of the system is assumed to be the complexity factor. We also look at the evolution of charged cylindrical matter source by selecting homologous pattern as the most basic evolutionary mode. In addition to this, homologous and complexity-free conditions are utilized to address dissipative as well as non-dissipative scenarios. The complexity producing parameters throughout the evolutionary process are assessed at the end. It is concluded that the complexity of the astrophysical entities is elevated due to the contribution of charge and modified terms of this theory.
theory. The self-gravitating objects possessing inhomogeneous energy density, pressure anisotropy, heat flux, charge and correction terms appear to encounter the complexity producing phase. Herrera’s orthogonal splitting method is used to identify the scalar functions in which the factor that incorporates all of the fundamental aspects of the system is assumed to be the complexity factor. We also look at the evolution of charged cylindrical matter source by selecting homologous pattern as the most basic evolutionary mode. In addition to this, homologous and complexity-free conditions are utilized to address dissipative as well as non-dissipative scenarios. The complexity producing parameters throughout the evolutionary process are assessed at the end. It is concluded that the complexity of the astrophysical entities is elevated due to the contribution of charge and modified terms of this theory.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




