https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04022-0
Regular Article
Empirical model for compound nucleus formation probability in heavy ion fusion reactions
1
Department of Physics, Government College for women, 563101, Kolar, Karnataka, India
2
Rajah Serfoji Government College(Autonomous), 613005, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu, India
3
Department of Physics, Ramakrishna Mission Vivekananda Educational and Research Institute, PO Belur Math, 711202, Dist Howrah, West Bengal, India
Received:
4
February
2023
Accepted:
22
April
2023
Published online:
14
June
2023
Compound nucleus formation probability (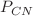 ) is very important to study the heavy ion fusion reactions forming superheavy nuclei. But we found only a few measurements performed as a function of energy till date utilizing eight heavy ion reactions. Accordingly, developing an empirical formula from the experimental data is difficult. However, one empirical formula is used to fit the experimental data, which is a function of projectile energy, fusion (Bass) barrier and three constants. These constants are different for different reactions and can only be known from experiment. Therefore, it cannot be used to predict these constants for any other reactions. To resolve this issue, we have developed a method to estimate these constants empirically as a function of beam energy, fusion barrier, Coulomb interaction parameter, and deformation parameter from five reactions and validated the model with other three reactions. Comparison of the present predictions with other models and experiments show that the present model is the best. We believe the proposed empirical formulae can be useful in the planning of the experiments for synthesizing the superheavy elements.
) is very important to study the heavy ion fusion reactions forming superheavy nuclei. But we found only a few measurements performed as a function of energy till date utilizing eight heavy ion reactions. Accordingly, developing an empirical formula from the experimental data is difficult. However, one empirical formula is used to fit the experimental data, which is a function of projectile energy, fusion (Bass) barrier and three constants. These constants are different for different reactions and can only be known from experiment. Therefore, it cannot be used to predict these constants for any other reactions. To resolve this issue, we have developed a method to estimate these constants empirically as a function of beam energy, fusion barrier, Coulomb interaction parameter, and deformation parameter from five reactions and validated the model with other three reactions. Comparison of the present predictions with other models and experiments show that the present model is the best. We believe the proposed empirical formulae can be useful in the planning of the experiments for synthesizing the superheavy elements.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




