https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03557-y
Regular Article
Consequences of baryogenesis phenomenon in  gravity
gravity
1
Department of Mathematics, COMSATS University Islamabad, 54000, Lahore, Pakistan
2
School of Mathematics and Statistics, Northwestern Polytechnical University, 710072, Xi’an, China
c jawadab181@yahoo.com, abduljawad@cuilahore.edu.pk
Received:
20
December
2021
Accepted:
16
November
2022
Published online:
3
January
2023
The baryogenesis is a hypothesized phenomenon which explains the matter–antimatter imbalance in the beginning of the universe. In this paper, we explore gravitational baryogenesis mechanism in the context of  theory of gravity, where R denotes the Ricci scalar and P encodes specific cubic contractions of the Riemann tensor. Baryogenesis is based on the coupling between the baryon matter current
theory of gravity, where R denotes the Ricci scalar and P encodes specific cubic contractions of the Riemann tensor. Baryogenesis is based on the coupling between the baryon matter current 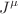 and the Ricci scalar curvature R, suggested by (Davoudiasl et al. Phys Rev Lett 93: 201301, 2004). For this mechanism, we assume that the cosmos is filled with perfect fluid. We consider five models for
and the Ricci scalar curvature R, suggested by (Davoudiasl et al. Phys Rev Lett 93: 201301, 2004). For this mechanism, we assume that the cosmos is filled with perfect fluid. We consider five models for  gravity and calculate the baryon number density to entropy ratio for each model. We also compute the generalized gravitational baryogenesis case, in which the CP-violating term is proportional to
gravity and calculate the baryon number density to entropy ratio for each model. We also compute the generalized gravitational baryogenesis case, in which the CP-violating term is proportional to 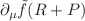 . We restrict the models using the cosmic gravitational baryogenesis scheme, highlighting the optimal model parameter values that are consistent with the observational data of baryon-to-entropy ratio (i.e.,
. We restrict the models using the cosmic gravitational baryogenesis scheme, highlighting the optimal model parameter values that are consistent with the observational data of baryon-to-entropy ratio (i.e., 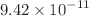 ).
).
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




