https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03494-w
Regular Article
A level set analysis of oil droplet division dynamics in an oil-in-water emulsion flow through a constricted splitting channel
Geo-Energy Research Institute, College of Electromechanical Engineering, Qingdao University of Science and Technology, 261550, Gaomi, China
Received:
11
July
2022
Accepted:
13
November
2022
Published online:
21
November
2022
The rheology properties accompanying the oil droplet division process lack in-depth discussions so far. In this paper, we numerically studied the oil droplet division dynamics in a two-dimensional O/W flow in a constricted splitting channel. The Navier–Stokes equations are solved numerically using the finite element method while the oil–water interface is tracked using the level set method. After validating the numerical scheme, the dynamic behavior of the oil droplet division is studied and the flow rheology properties are scrutinized. It is observed the droplet interface morphology variations lead to much higher average pressure drops in the droplet division process, which underlies the applicability of O/W emulsion in EOR practices. Then, systematic parameter investigations are performed on the effects of gravity, surface tension, and contact angle on the droplet flow dynamics. Gravity and surface tension are characterized in terms of Bond (Bo) and capillary (Ca) numbers, respectively, while the contact angle is denoted by 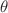 . It is found that the droplet splits asymmetrically and tends to push larger droplet volume to the upper branch under the high Bo number. And lower Ca lead to a drastic increase in the pressure drop and decay in the velocity. While a larger
. It is found that the droplet splits asymmetrically and tends to push larger droplet volume to the upper branch under the high Bo number. And lower Ca lead to a drastic increase in the pressure drop and decay in the velocity. While a larger 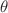 gives the convex shape of the droplet's rear and front, decreasing the average pressure drop and increasing the average fluid velocity. This work is expected to help understand porous media's O/W emulsion flow characteristics.
gives the convex shape of the droplet's rear and front, decreasing the average pressure drop and increasing the average fluid velocity. This work is expected to help understand porous media's O/W emulsion flow characteristics.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




