https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02885-3
Regular Article
Gravitational weak lensing by a naked singularity in plasma
1
Inha University in Tashkent, Ziyolilar 9, 100170, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2
Akfa University, Milliy Bog’ Street 264, 111221, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
3
National University of Uzbekistan, 100174, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
4
Department of Physics, Zhejiang Normal University, 321004, Jinhua, China
5
Centre for Theoretical Physics, Jamia Millia Islamia, 110025, New Delhi, India
6
Astrophysics and Cosmology Research Unit,School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Private Bag 54001, 4000, Durban, South Africa
a atamurotov@yahoo.com, f.atamurotov@inha.uz
Received:
13
March
2022
Accepted:
25
May
2022
Published online:
4
June
2022
Janis-Newman-Winicour (JNW) metric is the most general static spherically symmetric solution to the Einstein massless scalar equations with additional parameter  , encompassing the Schwarzschild metric as a particular case when
, encompassing the Schwarzschild metric as a particular case when  . It admits globally naked strong curvature singularity. We investigate weak-field lensing by JNW spacetime naked singularities when surrounded by plasma for three distributions: uniform, singular isothermal spheres and non-singular isothermal gas spheres. In the plasma’s presence, we find that the gravitational deflection differs from the vacuum deflection angle. The gravitational deflection angle in plasma depends on the frequency of a photon. In addition, the lens equation obtained the observed quantity of the Einstein angle and magnification of the image’s brightness for various specific parameters
. It admits globally naked strong curvature singularity. We investigate weak-field lensing by JNW spacetime naked singularities when surrounded by plasma for three distributions: uniform, singular isothermal spheres and non-singular isothermal gas spheres. In the plasma’s presence, we find that the gravitational deflection differs from the vacuum deflection angle. The gravitational deflection angle in plasma depends on the frequency of a photon. In addition, the lens equation obtained the observed quantity of the Einstein angle and magnification of the image’s brightness for various specific parameters  analytically and found that these expressions are modified compared to the lensing quantities for standard Schwarzschild black holes, which are regained as a particular case when
analytically and found that these expressions are modified compared to the lensing quantities for standard Schwarzschild black holes, which are regained as a particular case when 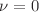 . We also discuss the influence of plasma on lensed images formed by photons. We find the deflection angle increases with JNW parameter
. We also discuss the influence of plasma on lensed images formed by photons. We find the deflection angle increases with JNW parameter  and plasma frequency in all the three cases, but the increase is sharp with
and plasma frequency in all the three cases, but the increase is sharp with  only. Interestingly, for a given
only. Interestingly, for a given  and plasma frequency, the deflection angle decreases with the impact parameter b
and plasma frequency, the deflection angle decreases with the impact parameter b
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022




