https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12150-7
Regular Article
Investigation of the thermal and microstructural changes of CuAlNiNb quaternary shape memory alloys by different niobium amount
1
Inonu University, Vocational School of Health Service, Malatya, Turkey
2
Fırat University, Faculty of Science, Department of Physics, Elazığ, Turkey
* e-mail: deniz.yakinci@inonu.edu.tr
Received:
11
April
2018
Accepted:
8
June
2018
Published online:
30
July
2018
Among the CuAl-based alloys, the most useful one is the CuAlNi ternary shape memory alloy. There are studies on the development of these alloys. In this study, 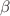 -Nb element was added to the CuAlNi alloy as a fourth element at various rates. The effect of the doped Nb element on the martensitic transformation temperature of the CuAlNi-shape memory alloy was determined by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). When the value of transformation temperature in quaternary CuAlNi alloys increased, as a result, austenite start and martensite start temperatures are close to each other. Crystalline structure analysis with X-ray diffractometer revealed that
-Nb element was added to the CuAlNi alloy as a fourth element at various rates. The effect of the doped Nb element on the martensitic transformation temperature of the CuAlNi-shape memory alloy was determined by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). When the value of transformation temperature in quaternary CuAlNi alloys increased, as a result, austenite start and martensite start temperatures are close to each other. Crystalline structure analysis with X-ray diffractometer revealed that 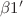 and
and 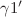 phases were found in Cu83.5Ni3.5Al13 alloy, which is the main alloy, while crystal structure of
phases were found in Cu83.5Ni3.5Al13 alloy, which is the main alloy, while crystal structure of 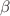 -Nb phase was also found with Nb addition. Likewise, the same phases were determined by SEM-EDX analysis. In addition, the result of Vickers hardness measurements indicated that the hardness value of CuAlNi alloys increased by extent of contribution of Nb.
-Nb phase was also found with Nb addition. Likewise, the same phases were determined by SEM-EDX analysis. In addition, the result of Vickers hardness measurements indicated that the hardness value of CuAlNi alloys increased by extent of contribution of Nb.
© Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature, 2018




