https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06680-8
Regular Article
Synthesis, structural, mechanical, thermal, and radiation shielding characterization of aluminum borosilicate glasses containing BaO and ZnO oxides
1
Department of Physics, College of Science, Princess Nourah Bint Abdulrahman University, P.O. Box 84428, 11671, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
2
Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Al-Azhar University, P.O. 71524, Assiut, Egypt
3
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Al-Azhar University, P.O. 71524, Assiut, Egypt
Received:
22
May
2025
Accepted:
21
July
2025
Published online:
3
August
2025
This study focused on developing novel, high-transparency, lead-free radiation shielding glasses with compositions of the form xBaO–17SiO₂–(20–x)ZnO–58B₂O₃–5Al₂O₃, where x ranged from 0 to 12 mol%. All glasses were prepared using a melt-quenching procedure. The increase in density from 3.374 to 4.087 g/cm3 is attributed to the rise in the average molecular weight. The introduction of BaO in a glass network can certainly enhance its mechanical properties, making it stronger and more rigid. The increase in resistance of glass samples to external forces in all directions is mainly reliant on the density. The increase of 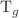 from 482 for AlZnBa-0 to 493 for AlZnBa-1.5, to 496 for AlZnBa-3, to 502 for AlZnBa-6, and to 506 for AlZnBa-12,
from 482 for AlZnBa-0 to 493 for AlZnBa-1.5, to 496 for AlZnBa-3, to 502 for AlZnBa-6, and to 506 for AlZnBa-12, 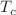 increases from 593 for AlZnBa-0 to 617 for AlZnBa-1.5, to 626 for AlZnBa-3, to 636 for AlZnBa-6, and to 643 for AlZnBa-12, and ∆T increases from 111 for AlZnBa-0 to 124 for AlZnBa-1.5, to 130 for AlZnBa-3, to 134 for AlZnBa-6, and to 137 for AlZnBa-12. The radiation shielding results indicated slight increases in MAC and Zeff, with added BaO. The MAC and Zeff variation as follows: AlZnBa-12 > AlZnBa-6 > AlZnBa-3 > AlZnBa-1.5 > AlZnBa-0. These findings enhance our understanding of how compositional variations influence the properties of the synthesized glasses.
increases from 593 for AlZnBa-0 to 617 for AlZnBa-1.5, to 626 for AlZnBa-3, to 636 for AlZnBa-6, and to 643 for AlZnBa-12, and ∆T increases from 111 for AlZnBa-0 to 124 for AlZnBa-1.5, to 130 for AlZnBa-3, to 134 for AlZnBa-6, and to 137 for AlZnBa-12. The radiation shielding results indicated slight increases in MAC and Zeff, with added BaO. The MAC and Zeff variation as follows: AlZnBa-12 > AlZnBa-6 > AlZnBa-3 > AlZnBa-1.5 > AlZnBa-0. These findings enhance our understanding of how compositional variations influence the properties of the synthesized glasses.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




