https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06657-7
Regular Article
Investigation of radon gas concentration and related radiation hazard parameters in different spices from Iraqi markets using CR-39 NTD
1
Department of Physics, College of Science, University of Thi Qar, Thi Qar, Iraq
2
Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Al-Nahrain University, Baghdad, Iraq
3
Department of Physics, College of Science, Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad, Iraq
a
raghad.almaliki@uomustansiriyah.edu.iq
Received:
30
May
2025
Accepted:
15
July
2025
Published online:
7
August
2025
This study aims to evaluate the radon concentration, radium concentration, emanation factor, and exhalation rates in spices available in Iraqi markets. For this purpose, a total of 12 spice samples were collected from different markets in Baghdad and Nasiriyah/Iraq. The radon concentration was determined using a CR-39 passive track detector. The radon concentration, radium concentration, emanation factor, mass, and surface exhalation rates were found to range from 19.87 ± 0.59 Bq/m3 to 25.44 ± 0.61 Bq/m3, 0.040 ± 1.56 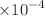 Bq kg−1 to 0.051 ± 2.05
Bq kg−1 to 0.051 ± 2.05 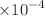 Bq kg−1, 1.87 to 2.02, 0.596 ± 0.003
Bq kg−1, 1.87 to 2.02, 0.596 ± 0.003 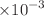
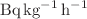 to 0.762 ± 0.003
to 0.762 ± 0.003 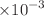
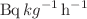 and 0.596 ± 0.003
and 0.596 ± 0.003 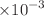
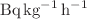 to 0.762 ± 0.003
to 0.762 ± 0.003 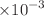
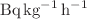 , with an average values of 21.95 ± 0.08 Bq/m3, 0.045 ± 1.57E
, with an average values of 21.95 ± 0.08 Bq/m3, 0.045 ± 1.57E 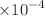 Bq kg−1, 1.95, 0.658 ± 0.002
Bq kg−1, 1.95, 0.658 ± 0.002 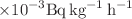 , and 1.341 ± 0.005
, and 1.341 ± 0.005 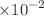
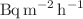 , respectively. These values were compared with the safe recommended limit values recommended by the international commissions. Consequently, it has been concluded that these values are well below the safe limit value (200 Bq/m3) and 150 Bq/m3 recommended by the International Commission on Radiological Protection and the Environmental Protection Agency of the United States, respectively. In addition, a strong positive correlation was found between radon concentration, radon activity, radium concentration, mass, and surface exhalation rate. These outcomes suggest that the spice samples pose no substantial radiological risk to the local community.
, respectively. These values were compared with the safe recommended limit values recommended by the international commissions. Consequently, it has been concluded that these values are well below the safe limit value (200 Bq/m3) and 150 Bq/m3 recommended by the International Commission on Radiological Protection and the Environmental Protection Agency of the United States, respectively. In addition, a strong positive correlation was found between radon concentration, radon activity, radium concentration, mass, and surface exhalation rate. These outcomes suggest that the spice samples pose no substantial radiological risk to the local community.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




