https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06612-6
Regular Article
A bionic auditory approach for coal gangue recognition based on gradient curling acoustic metamaterial and auditory perception
1
School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology, NO. 1, Daxue Road, 221116, Xuzhou, China
2
Institute of Intelligent Machines, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 230026, Hefei, China
3
Department of Automation, University of Science and Technology of China, 230026, Hefei, China
4
State Key Laboratory of Intelligent Mining Equipment and Technology, 221116, Xuzhou, China
5
Guangzhou GRG Metrology & Test Co. Ltd, 510627, Guangzhou, China
a
ysgcumt@163.com
b
liuhg@cumt.edu.cn
Received:
10
April
2025
Accepted:
2
July
2025
Published online:
21
July
2025
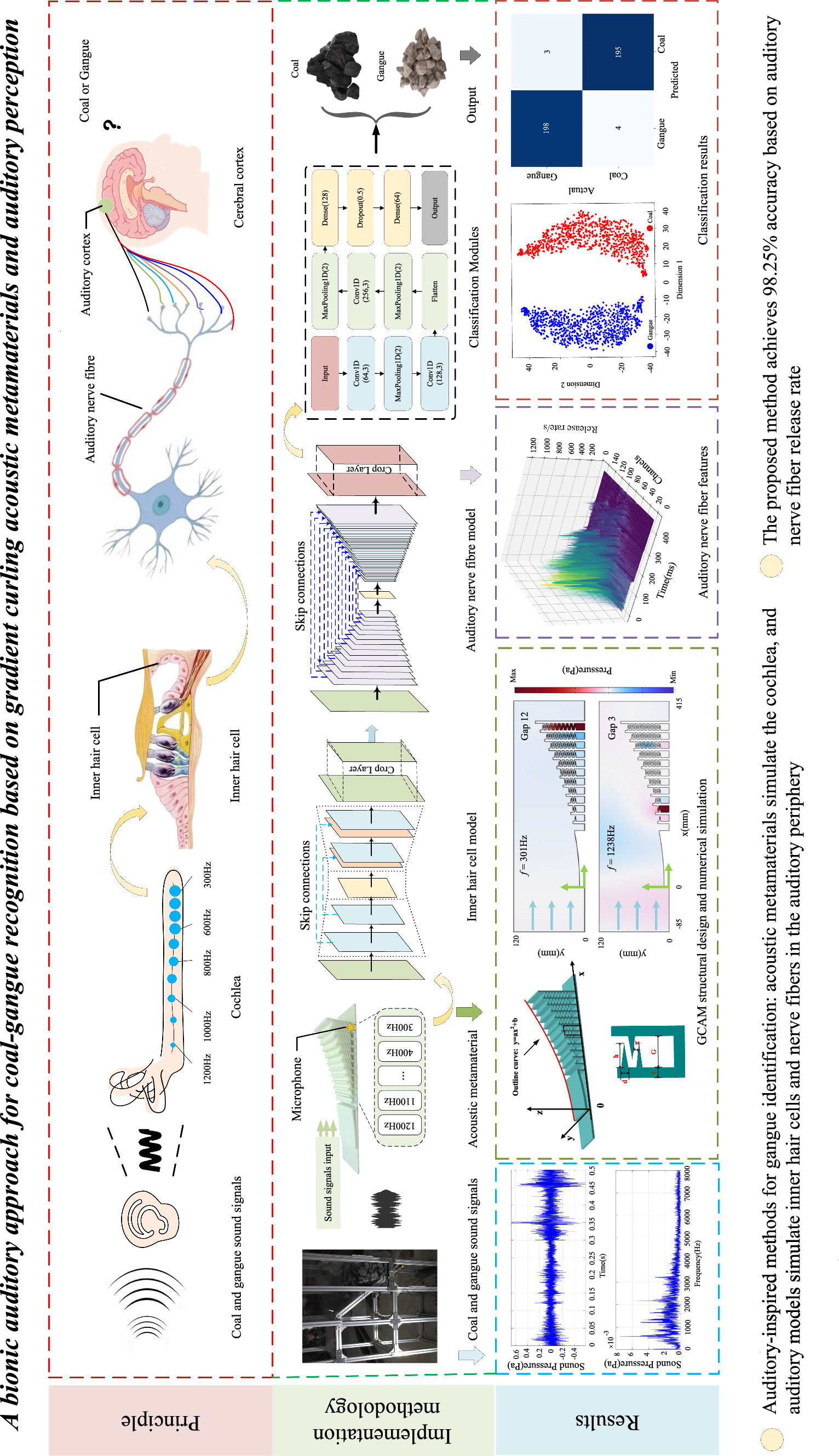
Top coal caving is one of the main ways to mine thick coal seams, and achieving intelligent coal gangue recognition is crucial to improve mining efficiency. However, the complex underground environment and strong background noise limit the practical application of existing coal gangue recognition algorithms. Inspired by the auditory system's ability to accurately recognize acoustic events in complex acoustic environments, this paper proposes a coal gangue recognition method based on an imitation auditory mechanism. The method includes an acoustic metamaterial module that mimics the cochlea and an auditory periphery module that simulates inner hair cells and auditory nerve fibers. First, mimicking the frequency-selective properties of the cochlear basilar membrane, a gradient curling acoustic metamaterial (GCAM) with specific frequency band filtering and frequency division functions is designed. Its structural parameters are optimized by numerical analysis. Subsequently, a computational module that simulates the auditory periphery, including inner hair cells and auditory nerve fibers, is constructed. The multi-channel sound signals after frequency selection and frequency division of the acoustic metamaterial are processed to extract the characteristics of the auditory nerve fiber release rate. Finally, the convolutional neural network is used to classify the auditory nerve fiber release rate features to achieve the accurate identification of coal gangue. The experimental results show that the recognition accuracy of this auditory-inspired method reaches 98.25%, which is significantly better than the traditional method.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.