https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06595-4
Regular Article
Deposition, characterization, and simulation of alternative electron transport layers (ZnO and 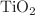 ) for performance optimization in CIGS-based solar cells
) for performance optimization in CIGS-based solar cells
Physics Department, Bilecik Seyh Edebali University, 11000, Bilecik, Turkey
Received:
10
April
2025
Accepted:
25
June
2025
Published online:
11
July
2025
Optimization of electron transport layers (ETLs) to enhance the electrical performance of CIGS (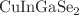 )-based solar cells has been investigated by experimental characterization and device simulation. ZnO and
)-based solar cells has been investigated by experimental characterization and device simulation. ZnO and 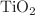 thin films were deposited on glass substrates using solgel spin coating method as alternative ETL materials to the conventionally used CdS layer. The structural, morphological and optical properties of these films were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy and UV–Vis spectroscopy. The optical band gaps of ZnO and
thin films were deposited on glass substrates using solgel spin coating method as alternative ETL materials to the conventionally used CdS layer. The structural, morphological and optical properties of these films were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy and UV–Vis spectroscopy. The optical band gaps of ZnO and 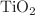 were determined to be 3.37 eV and 3.20 eV, respectively. Device simulations were performed with SCAPS-1D software under varying CIGS absorber thicknesses (2000–4000 nm) and operating temperatures (
were determined to be 3.37 eV and 3.20 eV, respectively. Device simulations were performed with SCAPS-1D software under varying CIGS absorber thicknesses (2000–4000 nm) and operating temperatures ( C) to evaluate their effects on key photovoltaic parameters. The simulation results showed that ZnO-based ETLs provided superior overall performance with a maximum efficiency of 17.14%, higher open-circuit voltage (Voc) and fill factor (FF) compared to
C) to evaluate their effects on key photovoltaic parameters. The simulation results showed that ZnO-based ETLs provided superior overall performance with a maximum efficiency of 17.14%, higher open-circuit voltage (Voc) and fill factor (FF) compared to 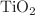 -based cells;
-based cells; 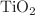 -based cells exhibited a lower efficiency of 14.25% despite a slightly higher short-circuit current density (Jsc). ZnO layers showed better thermal stability under temperature variation. This integrated experimental and simulation analysis shows that ZnO can be used as a promising ETL for high efficiency CIGS solar cells, while
-based cells exhibited a lower efficiency of 14.25% despite a slightly higher short-circuit current density (Jsc). ZnO layers showed better thermal stability under temperature variation. This integrated experimental and simulation analysis shows that ZnO can be used as a promising ETL for high efficiency CIGS solar cells, while 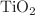 requires further material optimization to improve device performance.
requires further material optimization to improve device performance.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




