https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06566-9
Regular Article
Optical solitons in nematic liquid crystals: dynamics, stability and modulation instabilities
1
Department of Physics, Mody University of Science and Technology, Lakshmangarh, 332311, Sikar, Rajasthan, India
2
SciSER, Faculty of Science, Somaiya Vidyavihar University, 400077, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
3
Department of Physics and Materials Science, Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, 147004, Patiala, Punjab, India
Received:
1
May
2025
Accepted:
19
June
2025
Published online:
3
July
2025
The article investigates the nonlinear dynamics of Gaussian-shaped optical solitons in nematic liquid crystals exhibiting cubic-quintic nonlocal nonlinearity. The system is modeled using the nonlinear nonlocal Schrödinger equation and analyzed via the Lagrangian variational method and split-step Fourier method. Results confirm the existence of both low- and high-energy solitons, with their energy gap reduced approximately by 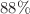 when medium shifted from local to nonlocal. Enhanced nonlocality also sharpens the potential profile, particularly for high-energy states. Linear stability analysis identifies stable and unstable regimes, while further examination shows that stronger nonlocality suppresses modulation instability. The quintic nonlinearity further reduces the instability bandwidth, and complete suppression occurs beyond a critical input power. These findings emphasize the crucial role of nonlocality and higher-order nonlinearity in soliton stability, offering insights for designing optical switching and photonic devices.
when medium shifted from local to nonlocal. Enhanced nonlocality also sharpens the potential profile, particularly for high-energy states. Linear stability analysis identifies stable and unstable regimes, while further examination shows that stronger nonlocality suppresses modulation instability. The quintic nonlinearity further reduces the instability bandwidth, and complete suppression occurs beyond a critical input power. These findings emphasize the crucial role of nonlocality and higher-order nonlinearity in soliton stability, offering insights for designing optical switching and photonic devices.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06566-9.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




