https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06554-z
Regular Article
Analytical solutions of stochastic partial differential equations in nanobioscience: exploring multiplicative noise effects
1
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt
2
Department of Mathematics, Basic Science Faculty, University of Bonab, Bonab, Iran
3
Research Center of Applied Mathematics, Khazar University, Baku, Azerbaijan
4
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, El-Arish University, North Sinai, Egypt
5
Department of Mathematics, College of Science, University of Duhok, Duhok, Iraq
6
Department of Physics and Engineering Mathematics, Higher Institute of Engineering, El–Shorouk Academy, Cairo, Egypt
7
Computer Engineering, Biruni University, Istanbul, Turkey
Received:
3
May
2025
Accepted:
10
June
2025
Published online:
15
July
2025
This paper presents a significant advancement in the study of stochastic partial differential equations within the context of nanobioscience, focusing on models that incorporate multiplicative noise. The main goal is to obtain precise solutions for these intricate equations, which is challenging due to the unpredictability brought about by stochastic elements. We utilize two advanced mathematical methods to achieve this: the refined Kudryashov’s technique and the 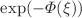 -expansion strategy. These methods allow us to derive various new exact solutions, such as kink-type wave solutions, straddled solitons, and singular solitons. A unique aspect of our research is the integration of a white noise term into our model, significantly enhancing the theoretical framework for stochastic partial differential equations in nanotechnology. This integration provides a closer match to actual phenomena and creates opportunities to investigate the behavior of nanoscale biological processes influenced by stochastic factors. The solutions we have identified highlight the value of our model in offering more profound insights into the complex behaviors observed in nanoscience systems, facilitating further theoretical and applied investigations in this cross-disciplinary area.
-expansion strategy. These methods allow us to derive various new exact solutions, such as kink-type wave solutions, straddled solitons, and singular solitons. A unique aspect of our research is the integration of a white noise term into our model, significantly enhancing the theoretical framework for stochastic partial differential equations in nanotechnology. This integration provides a closer match to actual phenomena and creates opportunities to investigate the behavior of nanoscale biological processes influenced by stochastic factors. The solutions we have identified highlight the value of our model in offering more profound insights into the complex behaviors observed in nanoscience systems, facilitating further theoretical and applied investigations in this cross-disciplinary area.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




